Hot spot in the data center: causes and effects
Accueil » Expertise » Data center » Hot spot in the data center: causes and effects
EOLIOS takes care of your data center:
- A passionate team
- Exclusive domains
- All sectors
- Data center
- A passionate team
Continue browsing :
Our latest news:
Our projects :
Our fields of intervention :
What temperature in a data center?
Ashrae standard
The Ashrae (American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers) data center temperature standard is a standardized recommendation for temperature management in data centers. This standard is regularly updated to take account of technological advances and industry best practices.
The Ashrae standard recommends a temperature range for data centers, rather than a specific temperature. The typical recommended range is between 18°C and 27°C (64°F and 81°F). This provides flexibility for data center operators, who can adjust the temperature to suit their specific needs.
One of the main aims of this standard is to optimize the energy efficiency of data centers while maintaining appropriate conditions for equipment operation. Temperatures that are too high can cause components to overheat and systems to fail, while temperatures that are too low can increase the risk of overheating.
Origin of hot spots in a data center
Explanation of the main thermo-aerodynamic phenomena
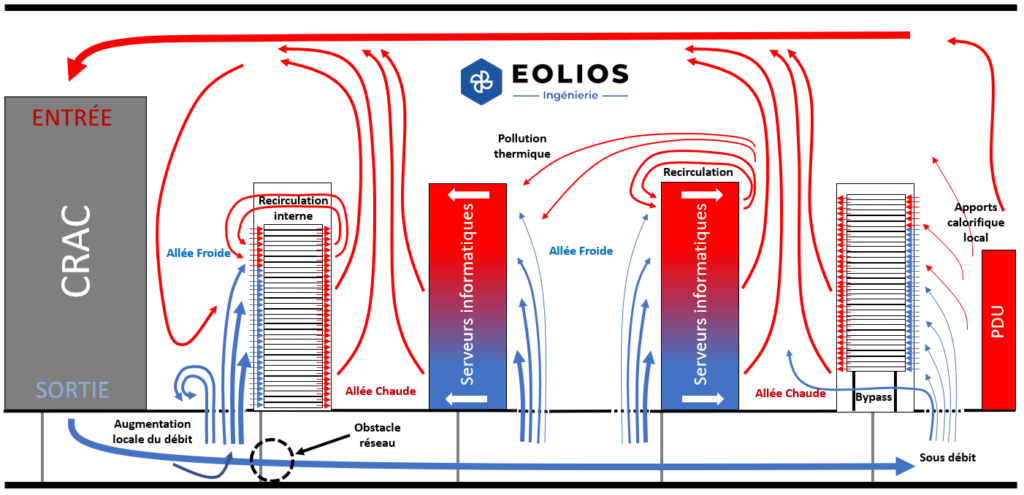
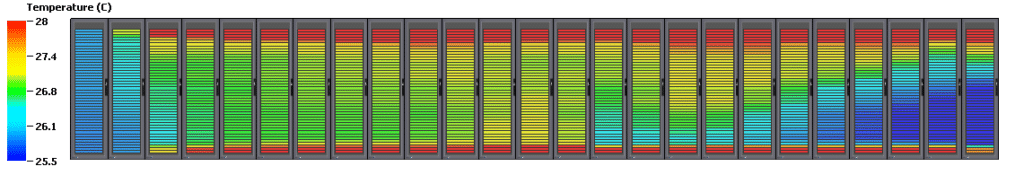
Hot spots in a data center are defined by ASHRAE TC 9.9 as areas where the air entering servers, storage systems, routers or other electronic equipment will be above 27°C. The rear area of the racks and areas in hot aisles are not considered hot spots. Hot spots can reduce reliability and damage electronic equipment due to the inability to dissipate the heat generated.
Server and hardware manufacturers may justify denial of warranty service due to violation of service contract terms by the presence of hot spots.
What parasitic air intakes can there be in a data center?
These are usually unsealed cable entries or cable duct entries from the computer room, air duct slots , slots at the bottom of load-bearing supports or simply holes in walls or doors. In the case of the raised floor itself, there may be openings for cable entry, openings under the cabinets, redundant perforated plates that may not be located in cold corridorsThere are openings in the floor around the computer room (behind the air control units, under the power distribution units).
Excessive cooling capacity in a data center can adversely affect
Surprisingly, a lack of cooling capacity is not the only cause of hot spots. Excessive cooling capacity can lead to hot spots. How can this happen?
If 8 cooling units are needed to cool the data center computer room, and 10 or 12 are installed and functioning, where, of course, each of the 10 or 12 units will operate with less power (than when only 8 units of cooling would have worked). This leads to a decrease in air supply and load, which in turn leads to additional hot zones in areas with low static pressure (dead zones).
Elimination of hot spots in the data center
Only the required number of perforated tiles need be installed in the cold corridors of the data center. Raised floor tiles should not be located in hot aisles or in unused space in the computer room. To calculate the number of perforated tiles required in the design of a data center, it is necessary to refer to the CFD studies of dimensioning.
The location of the diffusion grids must correspond to the thermal load of each cabinet. General guidelines for placement of slabs are shown in the table below.
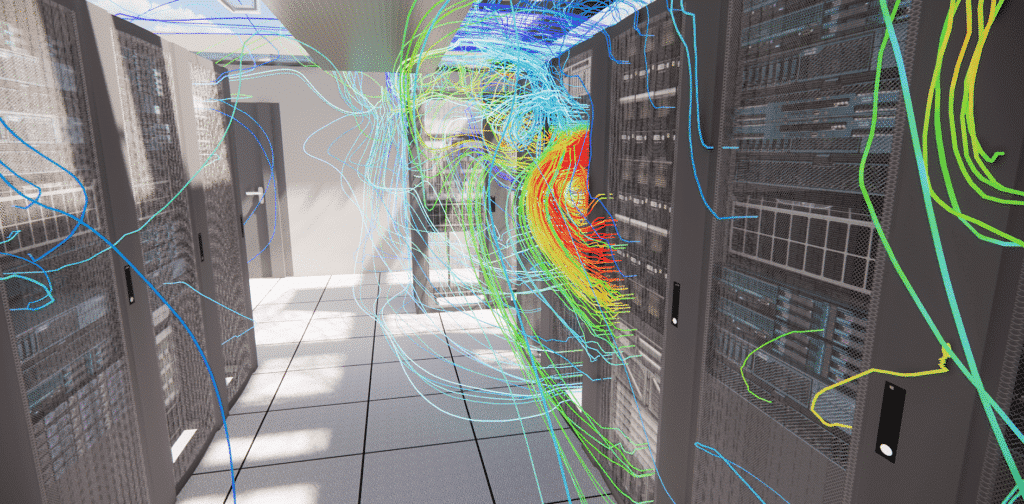
Why perform a CFD simulation of a data center?
CFD simulation provides information on the relationship between the operation of mechanical systems and changes in the thermal load of IT equipment. With this information, IT and site staff can optimize airflow efficiency and maximize cooling capacity.
It is also necessary to seal the cabinets of unused equipment. This involves installing blank blank blanking panels to cover any open space in the rack not occupied by the equipment. Also seal all side gaps between mounting rails and cabinet walls, openings at the bottom and top of the cabinets. Do not allow hot air to recirculate from the back of the cabinet to the front.
Free up as much space as possible under theraised floorfor better air circulation. Remove unused cables, debris, etc.
To check if everything has been done correctly, measure the temperature at the entrance of the server, especially on the top rows of the telecommunication cabinets. This can be done using a variety of thermometers: a non-contact IR thermometer; LCD strip thermometers or wireless RF temperature monitors. If the intake air is too cold or too hot, perforated plates can be added, moved or replaced. This check should be done regularly, especially when new equipment is installed or old equipment is dismantled.
Airflow simulation and CFD analysis
To take advantage of all these measures, it is necessary tocarefully study the heat load, the capacity of the cooling equipment and the airflow in the data center’s computer room.
Of course, additional costs will be incurred, but these costs are justified. According to the statistics of experts involved in theoptimization of the data center air conditioning system, the minimum reduction in energy consumption through the above actions is 10% to 36%.