File: applying IT246
Home » Smoke control » File: applying IT246
Understanding the Technical Instruction 246 [IT246]
In IT 246 the rules relating to smoke control are detailed in the special provisions applicable to each type of establishment. The purpose of this instruction is to clarify the rules of execution of smoke control by proposing solutions which guarantee: the sheltering of smoke or smoke control of stairways, smoke control of horizontal circulations and smoke control of premises accessible to the public.
Our projects :
Understand how air conditioning works in a data center
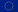
Natural draft smoke removal is achieved by using natural smoke vents and air inlets that are positioned to ensure proper sweeping of the area. These elements communicate directly with the outside or through conduits.
Smoke evacuation is provided by either:
- Outlets;
- Facing openings;
- Mouths.
The air supply is provided by either :
- Opening in front of the building
- The doors of the rooms to be cleared of smoke opening on the outside or on volumes that can be widely ventilated;
- Unenclosed stairs;
- Mouths
No opening shall be smaller than 20 centimeters.
In the case where the volume to be de-smoked is semi-buried and the air supply cannot be natural, then exceptionally mechanical air supplies can be used. They can only be associated with roof vents as a type of exhaust and the air velocity at the outlet is limited to 5 m/s.
Chilled water system
Smoke extraction by mechanical draught is carried out by mechanical extractors as well as natural or mechanical air supplies distributed so as to ensure a sweep. In addition to the smoke sweeping, it is possible to add an overpressure to the spaces to be protected from smoke.
Smoke extraction and mechanical air supply are provided by vents connected to an extraction fan.
As previously stated, the air velocity at the air inlets should not exceed 5 m/s. They must also have a flow rate of approximately 0.6 times the extraction rate.
Supply air flow = 0.6 x exhaust air flow
Smoke extraction fans must comply with the NF EN 12101-3 standard and be CE marked. The fans must be able to withstand hot fumes of 400°C for 90 minutes. Fan sizing must take into account leakage and pressure drop losses.
Chilled water system
For natural smoke ventilation, the following two rules must be respected by the ducts in order to solve the problems related to the generated pressure losses:
- The ratio of the largest dimension to the smallest dimension must be ≤ 2 ;
- The cross-sectional area of the duct must be equal to or greater than the free area of the outlets it serves.
Vertical venting may not have more than two offsets with a maximum angle of 20 degrees.
Draglines, which are the horizontal floor connections of the exhaust ducts, shall be a maximum of 2 metres in length unless adequate flow is demonstrated. To justify this flow rate, a calculation must be made assuming that the flue gas temperature is 70°C, that the outside temperature is +15°C and that there is no wind.
What is the difference between CRAC and CRAH units?
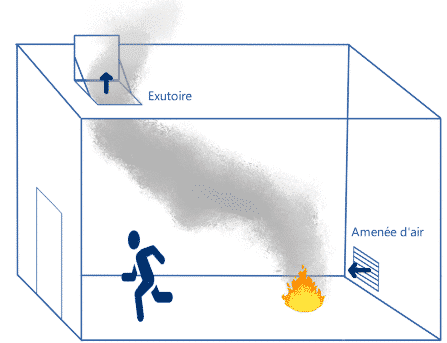
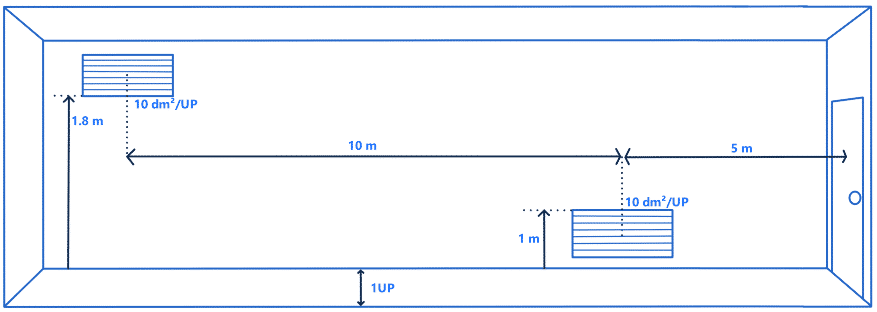
- The installation of the air supply and exhaust outlets is done in an alternating way. In the case of a straight circulation, the maximum distance between the air supply and the exhaust is 10 meters, if the circulation is not straight, the maximum distance is 7 meters. To place the first mouth, it is necessary to measure 5 meters from the axis of the first door accessible to the public.
- Air intakes must be no more than 1 meter above the floor,
- Smoke evacuations It is required that the lower part of the ducts be located at least 1.8 meters above the ground and that they be entirely positioned in the upper third of the circulation area.
- Free area of 10 dm² per unit of passage, in case there is only one extract unit for two air supply units, then the extract unit must have a free area of 20 dm² per UP.
What is the optimal temperature for a data center?
Sizing rules :
Premises ≤ 1 000 m²
Effective surface area of smoke extraction :
- Minimum of 1/200 of the area of the premises or be calculated by means of the table serving the premises of more than 1,000 m² with the rate α,
- Free surface of the air intakes: corresponding to the value of the geometrical surface of the smoke evacuations.
Premises > 1,000 sqm
- DENFC floor area:determined by the type of operation (building class) and based on the α rate.
- Minimum township value of 1,000 m² (even if less),
- Useful area = Rate α * Township area,
- Free surface of the air intakes: corresponding to the value of the geometrical surface of the smoke exhausts.
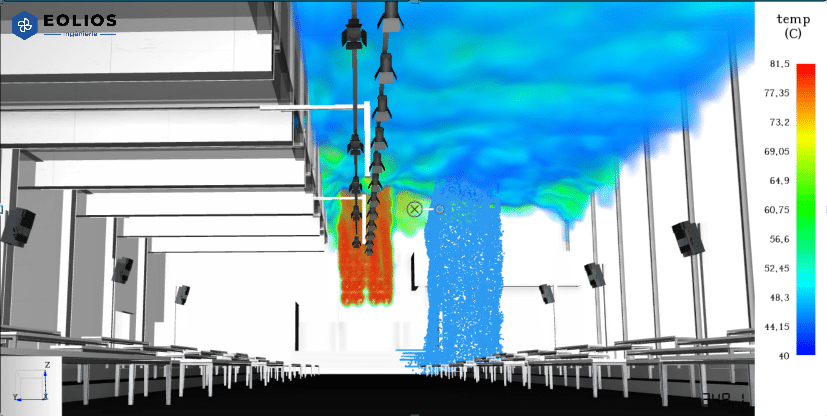
External CFD simulation of a data center
CASE N°2 : Stairs
Sizing rules :
The natural sweep of a stairwell is achieved by an evacuation device located :
- On the roof with a geometrical surface (Av) of 1 m² or on the façade with a free surface (SLC) of 1 m² located in the upper part of the cage,
- AND in both cases,an air supply located in the lower part of the cage of 1 m² of free surface (SLC).
- The control device is located on the lower level of the staircase,
- Resetting (closing) must be possible from the bottom of the stairs or the last landing
Natural smoke extraction from stairways is a system independent of the facility’s fire safety system.
Stairway smoke removal installations are qualified in the NF S61-932 standard of July 2015. If natural smoke extraction is not possible, the staircase must be pressurized by a mechanical air supply and must be associated with the smoke extraction of the volume in direct contact.
Smoke extraction engineering - Stairs with a roof vent
External CFD simulation of a data center
CASE N°3 : Smoke extraction room
Sizing rules :
The determination of the smoke clearing sections is defined in the technical instruction 246 (IT246)
- Canton mandatory for premises larger than 2,000 m² or more than 60 meters in length,
- The maximum area of a block is 1,600 m² or 60 meters in length,
- Smoke layer thickness:
- If the Height ≤8 m: smoke layer between 25% and 50% of the reference height,
- If the height > 8 m: smoke layer between 2 meters and 50% of the reference height,
- The smoke clearance height (SCH) must not be less than 1.8 meters,
External CFD simulation of a data center
Smoke control : on the same subject

Brandschutztechnik

Smoke extraction in underground parking lots
Sprinkler: how does a sprinkler system work?

Fire safety engineering

Data center fire safety: Automatic Gas Extinguishing Systems (IEAG)

File: applying IT263 – smoke extraction from atriums

The ESSOC law for fire safety

The objectives of smoke control

Dynamic modeling of the evacuation of people