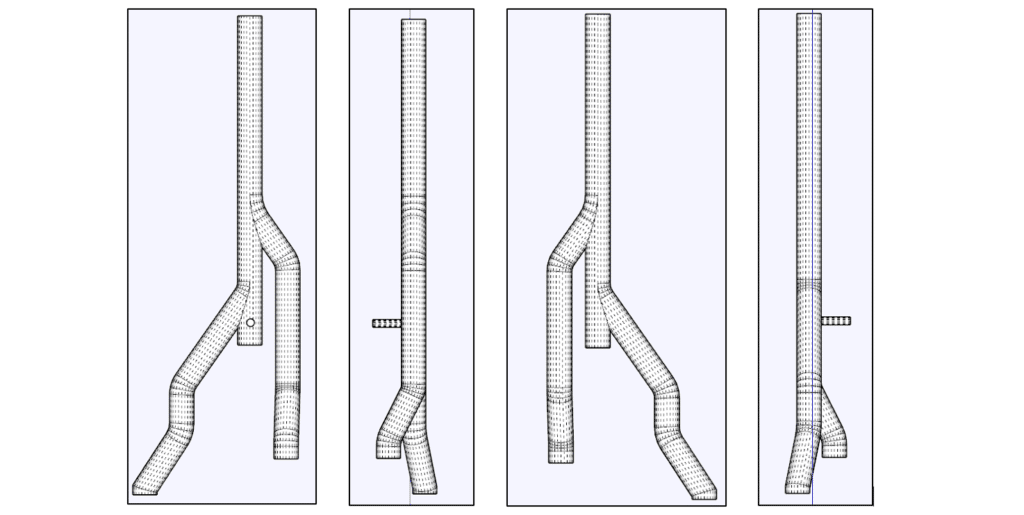
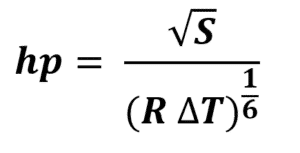Industrial chimney sizing
Home » Industrial Process » Industrial chimney sizing
EOLIOS designs chimneys for industrial equipment
We calculate regulatory discharge heights and carry out specific CFD simulations for industrial stack sizing.
- Regulatory height
- Erosion study
- Calculating pressure losses
- Thermal draft calculation
- Wind resistance
- Pollution study
Our projects :
Design and sizing of industrial chimneys and flues
Use our CFD simulation expertise to optimize your plant's operation
Asexperts in CFD simulation (fluid mechanics), our company specializes in the dimensioning of industrial chimneys and ducts.
The design and dimensioning of these structures are of crucial importance to ensure optimal operation of industrial plants. We put our know-how and expertise at your disposal to support you in this key stage of your project.
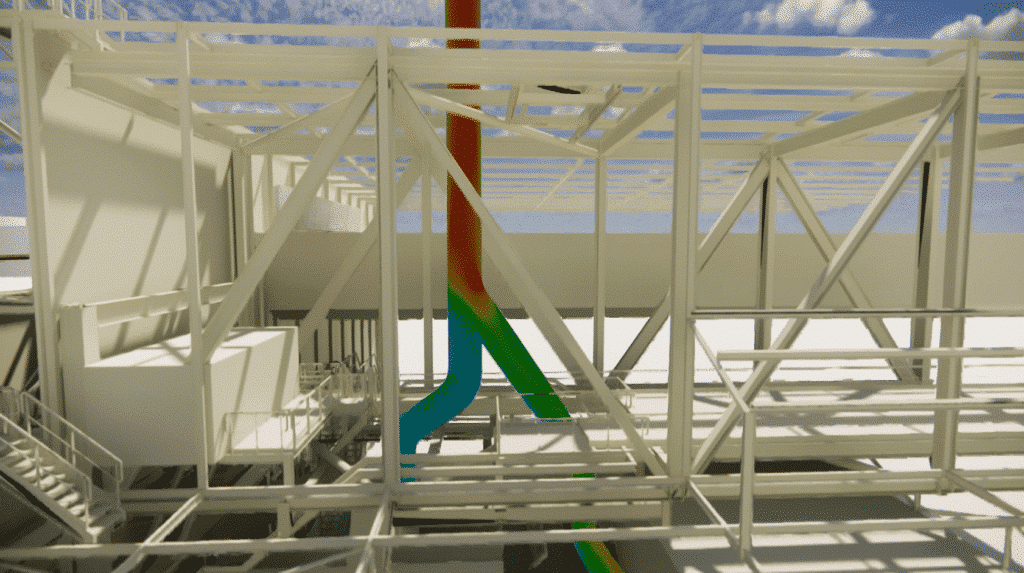
Using advanced CFD simulation software, we are able to accurately model fluid flows in stacks and ducts. This enables us toanalyze key parameters such as air velocity, pressures, temperatures and pollutant concentrations.
Using numerical models, we can simulate actual operating conditions and identify potential problems, such as reduced flow velocity, instabilities or vortex formation. Thanks to these in-depth analyses, we are able to propose optimized solutions for the safe and efficient operation of your industrial chimneys and ducts.
What are the rules for sizing an industrial chimney?
Dimensioning rules for combustion chimneys
The evacuation of combustion fumes is an essential step in the process, because of its impact on the environment as well as on the safety and comfort of operators.
Proper chimney sizing is therefore a key step, and is governed by regulations.
The chimney’s main function is to act as a smoke extractor.
Thanks to its height, it creates a vacuum that extracts combustion fumes from the combustion chamber when connected to a furnace.
The second role of the chimney is to discharge combustion fumes and dissipate them in the most efficient way possible, i.e. by raising them as high as possible to promote their dispersion and thus reduce their impact on the environment.
If the environmental height calculation (defined by regulatory texts) indicates a higher height than that required for the intake, this higher height will be taken into account.
There is no legal obligation to do so, but there is a standard(NF EN 13084-1, September 2007) recommending that chimneys be checked every two years.
In terms of outdoor safety, this is similar to building maintenance.
However, the particularity of chimneys lies in the fact that they are exposed to high temperatures and numerous acid attacks from smoke, whether they are made of metal, concrete or brick.
It is therefore essential to check regularly that these attacks are not damaging the chimneys.
Main standards to be met
The main regulations are as follows:
- Code de l’environnement : Article R224-18
- Order of February 2, 1998 articles 52 to 63
In addition to these texts, there are complementary documents:
- Standard NF EN 13084-1, September 2007: Freestanding chimneys – Part 1: general requirements
- Standard EN 1990 – EUROCODES, March 2003: Structural Eurocodes – Design bases for structures
- Standard EN ISO 14122-1, March 2017: Safety of machinery – Permanent means of access to machinery
- Combustion data sheet
These texts and standards provide guidelines and criteria to be taken into account for chimney sizing, safety and compliance, as well as for the management of environmental impacts associated with combustion smoke exhaust.
Regulatory calculation of chimney height
The height of the chimney is determined in metres by two factors:
- atmospheric pollutant emission levels
- the presence of obstacles that could impede gas dispersion.
This measurement, which may not be less than 10 meters, is established by the authorization order in accordance with articles 53 to 56 of the order of February 2, 1998, or it is calculated on the basis of the results of a study of gas dispersion conditions specifically adapted to the site.
Where
- S is calculated as: s = k q/cm for each of the main pollutants where :
- K: is a coefficient of 340 for gaseous pollutants and 680 for dust;
- q : is the maximum instantaneous theoretical flow rate of the pollutant in question emitted through the stack, expressed in kilograms per hour ;
- cm: is the maximum concentration of the pollutant considered admissible at ground level due to the installation, expressed in milligrams per normal cubic meter;
- cm: is equal to cr – co where cr is a reference value given in the table below and co is the annual average concentration measured at the site in question.
Correction of regulatory height according to site
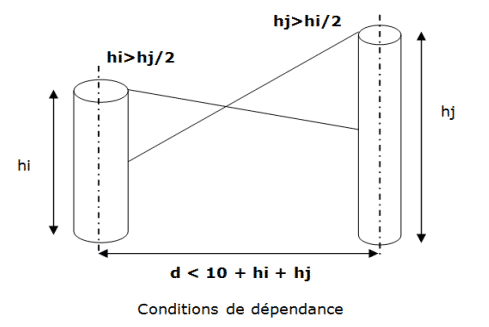
For two stacks i and j, with respective heights hi and hj calculated in accordance with article 54 of the decree of February 2, 1998, they are considered dependent if the following three conditions are simultaneously satisfied:
- The distance between the axes of the two chimneys is less than the sum of their heights plus 10 metres: (hi + hj + 10).
- The height hi is greater than half the height hj.
- The height hj is greater than half the height hi.
In this way, the set of stacks dependent on the stack in question is determined, the height of which is at least equal to the value of hp calculated for the total mass flow rate of the pollutants in question and the total volume flow rate of the gases emitted by all these stacks.
If there are natural or artificial obstacles in the vicinity that could interfere with gas dispersion, the stack height is corrected as follows:
If there are natural or man-made obstacles in the vicinity likely to interfere with gas dispersion, the stack height is corrected.
To comply with the decree of February 2, 1998, industrial chimneys must measure a certain regulatory height.
However, it’s not just the height of the chimney that must be taken into account.
Other criteria need to be taken into account, such as the level of draught, pressure drops, dilution flows and the risk of accidental pollution.
The study of industrial networks using CFD simulation
Optimization of industrial stacks through specialized CFD simulation studies
Fluid mechanics studies applied to industrial stacks are essential to ensure optimal operation of these installations.
As experts in CFD simulation (fluid mechanics), we specialize in these key studies.
Our expertise enables us to carry out various studies for industrial chimneys, such as :
– Thermal draft study: We evaluate the chimney system’s ability to create sufficient draft to evacuate smoke and flue gases.
Using advanced simulations, we take into account parameters such as chimney height, flue gas temperature, temperature difference between the inside and outside of the chimney, and local environmental conditions.
– Calculating pressure losses: We analyze pressure losses in the chimney, due to friction between moving gases and the chimney walls.
This study enables us to determine the pressure available for draft, and to optimize chimney design in terms of sizing and choice of materials.
– Erosion due to dust in flue gases: We study the impact of dust particles in flue gases on chimney walls.
Using advanced simulations, we identify areas at risk and recommend appropriate protective measures, such as the use of anti-abrasion materials or dust collection devices.
– Atmospheric dispersion analysis: We analyze the dispersion of combustion gases in the atmosphere, taking into account air quality regulations.
Using precise simulations, we assess gas dispersion from the stack, taking into account local meteorological conditions.
– Structural stability analysis: We assess the chimney’s resistance to external loads, such as wind and earthquakes.
This study enables us to guarantee the structural stability of the chimney, and to recommend modifications or reinforcements if necessary.
– Dew point analysis: In a pressurized industrial duct, dew point analysis is of vital importance, as it determines whether moisture in the duct could condense and lead to problems such as corrosion or frost formation.
Industrial chimney design with EOLIOS
EOLIOS ingénierie: Your trusted partner for dimensioning industrial chimneys and ducts in compliance with standards and regulations
Our team of experts has extensive experience in CFD simulation and in-depth knowledge of current standards and regulations.
We are able to take into account all relevant parameters to offer you tailor-made solutions, adapted to your specific needs.
When you work with us, you’ll benefit from first-rate expertise, personalized advice and support throughout the sizing process of your industrial chimneys and ducts.
Our aim is to help you maximize the performance of your installations while ensuring compliance with current environmental and safety standards.
Please contact us for more information about our expert services in industrial chimney and duct sizing.
We’ll be delighted to discuss your project and propose solutions tailored to your specific needs.