Home » Air & Wind » Numerical simulation of pedestrian comfort in an urban environment » Wind study – La Défense
Wind study – La Défense
In a few words
EOLIOS carried out a CFD study of the defense district.
Wind study - La Défense
Year
2023
Customer
NC
Location
France
Typology
Air & Wind
Continue navigation :
Our other projects :
Latest news :
CFD study: understanding air flows around a building for the implementation of wind energy systems
Our EOLIOS engineers bring their technical expertise to bear in understanding and modeling large-volume outdoor airflow in relation to CFD studies.
This document is an extract from a study of air velocities and trajectories around a planned building in France. The aim of the study is to verify the feasibility of implementing wind power systems for the building’s electricity production, then to propose alternatives for optimizing their performance, and to evaluate and assess the evolution of majority winds on site around the building in question.
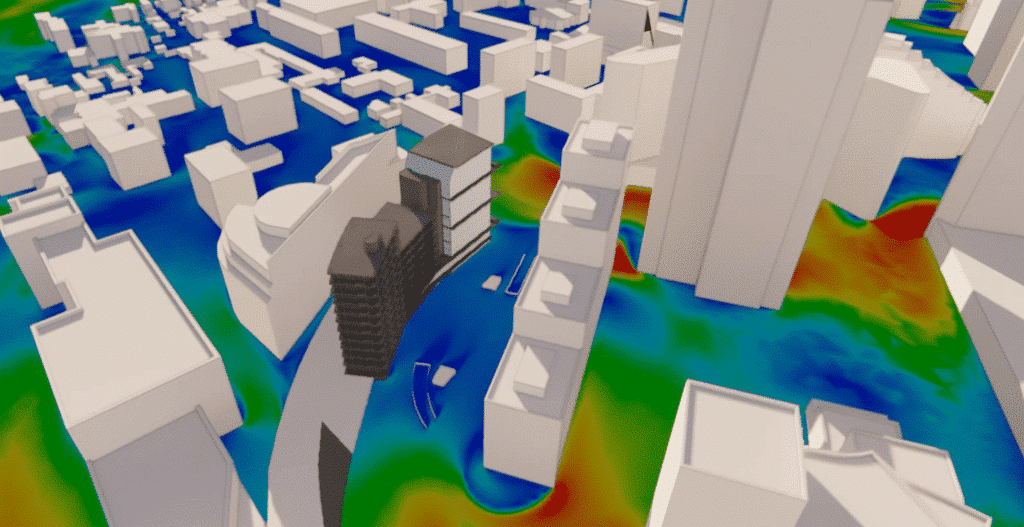
The defense district has a high density of buildings per m2, giving rise to numerous aeraulic masks. This characteristic of the district is of great importance in the evolution of airflow.
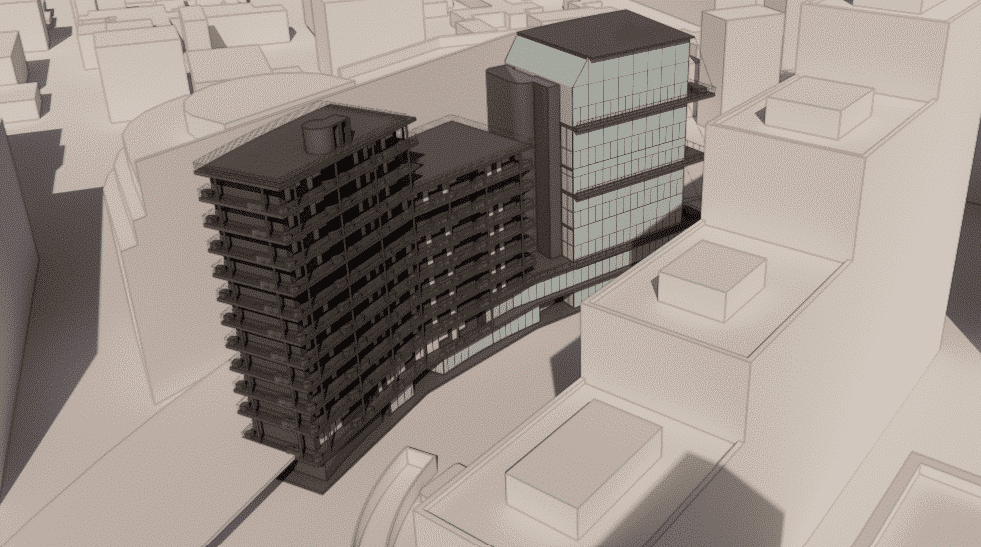
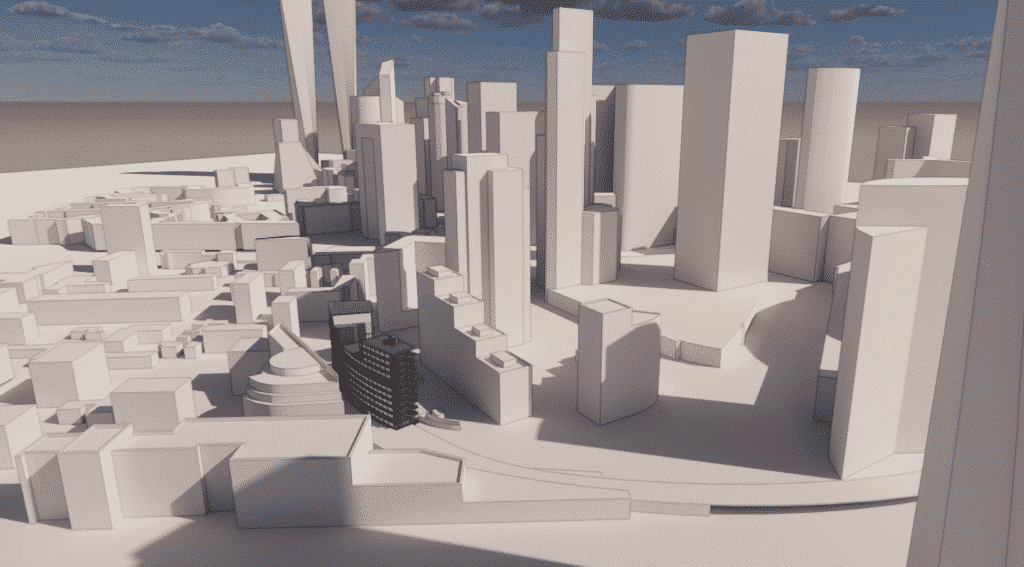
Realistic 3D model of La Défense
For this simulation, a large part of the buildings close to the project were modelled in order to take into account the particular conditions of the site being a specific location of high housing density and high buildingsIn addition, an extra level of precision was applied to obtain a more accurate result with regard to aeraulic masks.
The external CAD model produced shows the simplified geometry of the site and its surroundings within a 400m radius. It is based on the plans supplied.
Optimizing air comfort for pedestrians
Study of ground air speeds
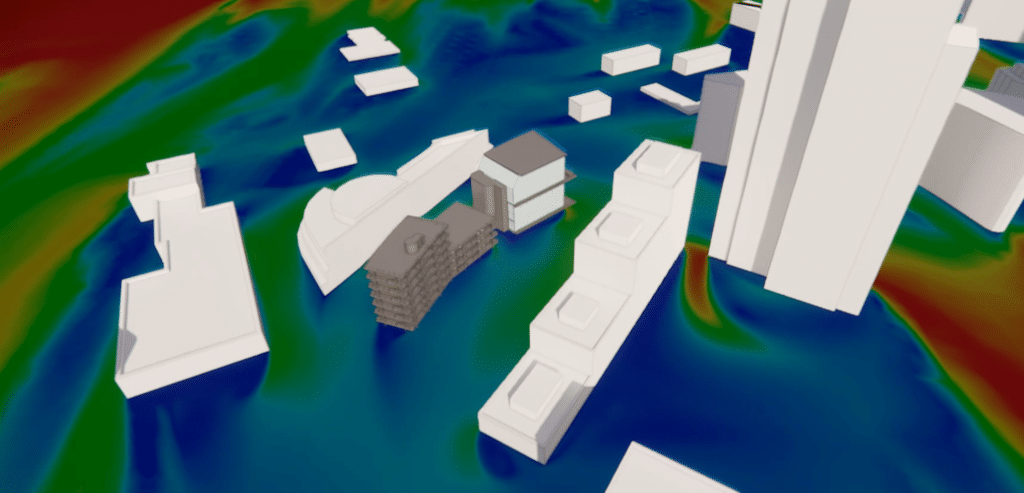
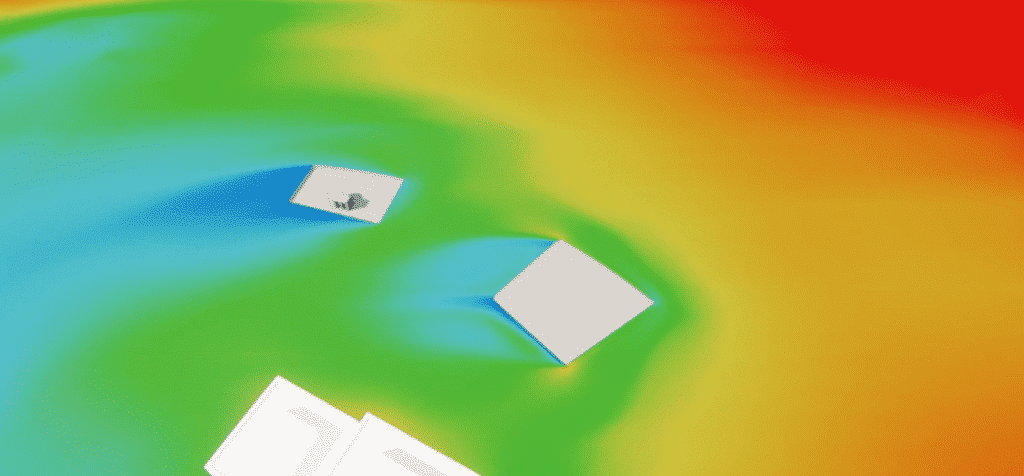
For a north-easterly wind, a number of specific aeraulic phenomena can be observed. For this wind direction, air speeds at ground level are of the order of 1.5 to 2 m/s.
The wind tends to blow towards Square Henri Regnault for two reasons:
- The restriction of airflow between the Les Dauphins residence and the Gambetta tower gives rise to a Venturi effect .
- The wind passing under the Boulevard Circulaire tends to redirect the air towards the square.
Current path around the project building
Venturi effect and building protection: simulation results for a specific wind direction
Study of ground air speeds
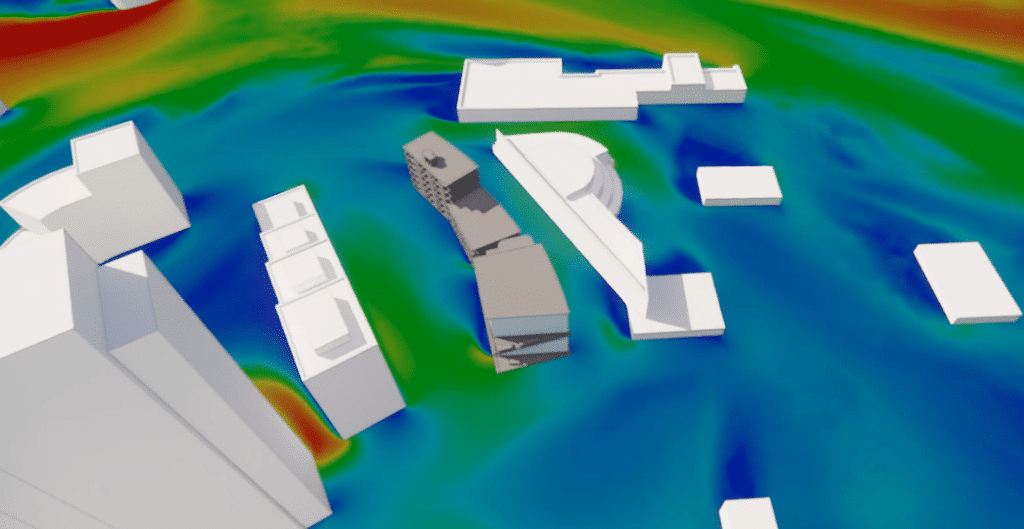
For a south-westerly wind, a number of specific aeraulic phenomena can be observed. For this wind direction, ground air speeds are of the order of 1.5 to 2 m/s close to the building’s south façade.
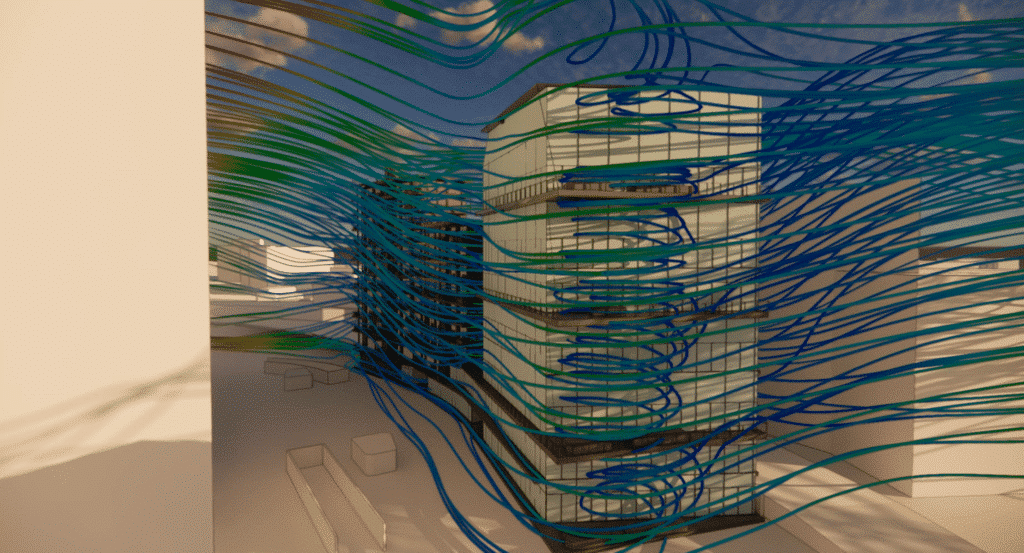
We note that the wind tends to blow between the project building and the Les Dauphins residence.
The simulation results show that the restriction of airflow between the Les Dauphins residence and the south-west building of the square gives rise to a Venturi effect accelerating the air towards the project building.
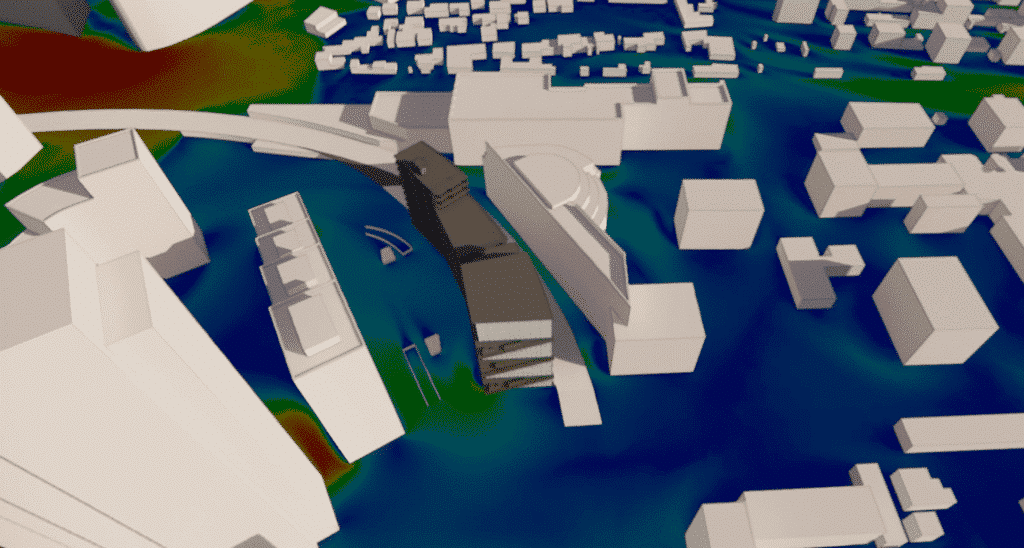
Air velocities at 40 m above ground are of the order of 1.5 m/s.
The simulation shows that for this wind direction, the Les Dauphins residence provides a sufficient aeraulic mask to protect a large part of the project building.
This aeraulic mask greatly reduces velocities when approaching the roof. Therefore, no overspeed due to wall separation was observed.
Optimizing building morphology to meet the challenges of urban comfort
CFD simulation: a response to the complex challenges of building design
Numerical simulation offers new perspectives for design offices. This makes it possible to foresee a large number of scenarios, and therefore to control any unforeseen events linked to poor design. In the case of new buildings, renovations or new layouts, multiphysics modelling can take into account all the phenomena that cause heat and air flows.
Study of ground air speeds for a south-westerly wind
CFD simulation: EOLIOS expertise in fluid mechanics and numerical simulations
Thanks to its calculation servers, EOLIOS models can be simulated in their entirety with great precision in a very short space of time. What’s more, EOLIOS’ experience in general aeraulics enables our team to propose innovative and relevant solutions in the aeraulics field. Implementing CFD simulations in your design process means calling on experts in fluid mechanics, thermal engineering and numerical simulations to ensure that no problems arise in the future.
Our EOLIOS engineers have extensive experience in auditing, bringing their expertise directly to bear to optimize the resolution of various problems.
Their cutting-edge equipment enables direct and distinct measurements, guaranteeing an assessment of the site, equipment and materials, and if necessary, a thermal expertise including thermal bridges, heat loss and loss of performance of air-conditioning systems.
Continue on this topic
Video summary of the study
Discover other projects
Study of aeraulic comfort – Middle school
Wind comfort study – Rooftop
Wind impacts on high-rise buildings: Tours Olympiades in Paris
Comfort – Rooftop of a palace – Casablanca
Tour Liberté – La Défense
Impact of wind on a solar power plant
Cooling towers – ICPE
Pedestrian comfort study – La Défense
Confort au Vent – PSG training center
Wind study – La Défense
Fine particle capture in a metro station
Sharaan by Jean Nouvel resort
Air coolers – Critical study – Heat wave
Fine dust measurements
Balenciaga – Wind potential