Understanding Technical Instruction 263 [IT263]
Some architectural projects often provide for the creation of an open space such as a courtyard or an interior street, surrounded by levels of various purposes (stores, offices, hotel rooms, etc.), which may or may not be covered. However, if a fire occurs in or near this space, it can lead to rapid spread of fire, smoke and hot gases. This technical instruction aims to establish the construction rules and the principles of smoke removal for these spaces, and applies to establishments of the first group as well as to establishments of the second group where the enclosure of stairways is required.
Download technical instruction 263 in .pdf format
Smoke control
Resources
Continue navigation :
Table of contents
Our latest news :
Read more :
Our projects :
Our areas of expertise :
Linkedin
Tiktok
Youtube
Video
Need an expert opinion?
Our engineers are ready to listen and take on any challenge.
Contact us
Smoke control engineering and IT263
This technical instruction proposes solutions to meet the smoke sheltering requirement for certain configurations. However, the constructions that do not correspond to these configurations require a particular study by the Central Security Commission after the opinion of the Departmental Consultative Commission of Security and Accessibility.
For example, lobby hoppers and interior streets also require appropriate smoke control based on their specific configuration. These smoke vents must be installed after the competent safety commission has given its opinion, under the same conditions as for the volumes to which they are assimilated, without taking into account the specific architectural provisions of these volumes. An order of March 22, 2004 specifies that the hoppers forming a hall must be cleared of smoke in accordance with Technical Instruction No. 246.
Understand how air conditioning works in a data center
The term “atrium” is used throughout the text to refer to the open interior volume, including atriums, patios, skylights, etc. We can distinguish three kinds of atrium:
Open air atrium:
It is the free volume closed on all its lateral faces, the smallest dimension of which is less than or equal to the height of the highest façade and which does not have any occlusion in the upper part
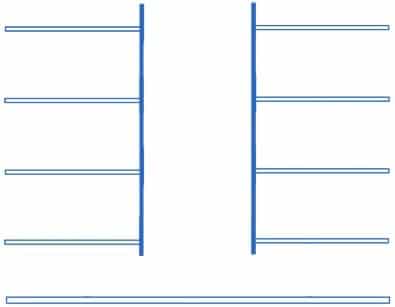
Open covered atrium:
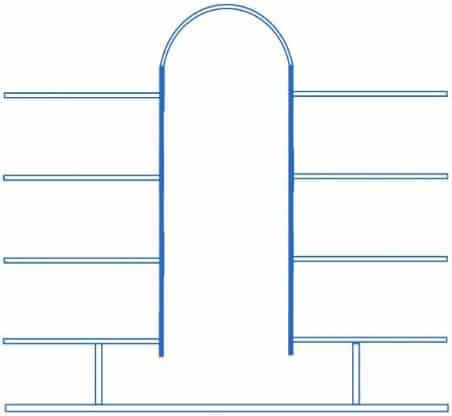
It is the same volume as the open air atrium with full or partial coverage. It is distinguished by the presence of levels permanently open to the central volume.
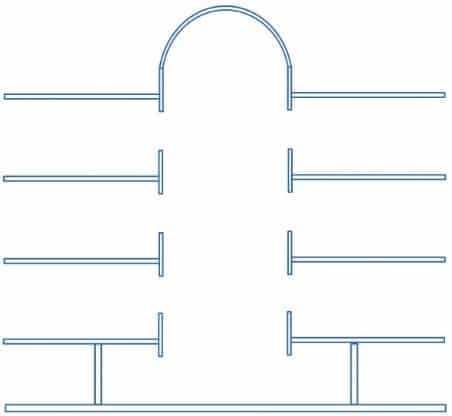
Covered atrium :
This type of atrium has all its levels closed by a wall.
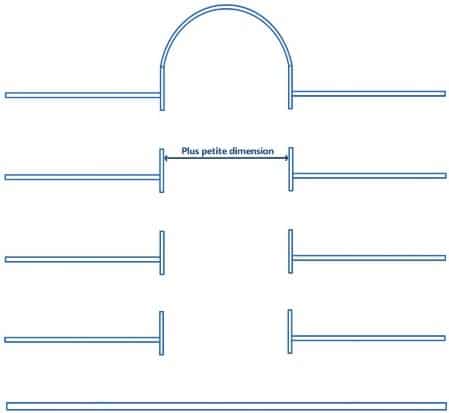
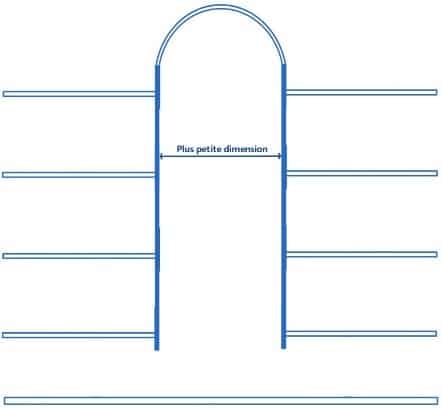
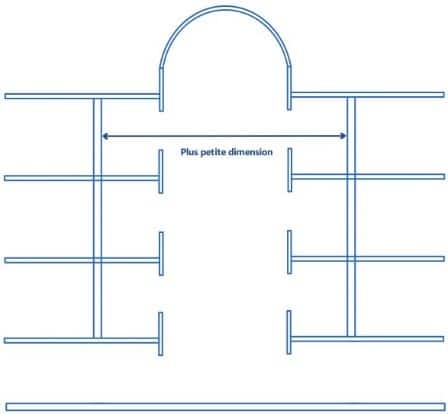
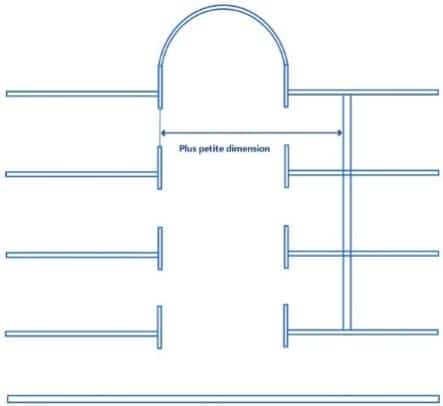
Smallest dimension of an atrium:
It is defined as the diameter of the right cylinder inscribing itself, over the entire height of the atrium, in the free space between :
- balcony noses for open atriums ;
- vertical walls for closed atriums ;
- balcony nosings and vertical walls for atriums open on one side and closed on the other
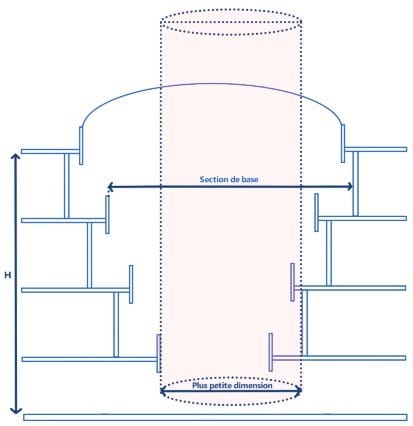
Basis of calculation for smoke control :
The base section of the atrium is the largest of the horizontal sections between the building elements delimiting the atrium (balcony nosings and/or vertical walls).
At each level, the cross-sectional area of the void between building elements shall be at least one-half of this base area.
The base volume of the atrium is the product of this base section and the total height of the atrium, measured at the ceiling of the top level.
Cold aisle / hot aisle design
Definition
According to convention, an atrium, whether covered or open-air, is a space whose smallest dimension is at least equal to √7H (H being the height between the lowest floor of the highest level and the lowest level of the atrium), but not less than 7 meters.
Smoke extraction in covered atriums
- The free surface of the smoke evacuations can be realized either by outlets or by openings placed on different facades. In the operating position, the closing device for these openings must not impede the normal flow of smoke.
- For natural smoke ventilation, air inlets must have a free surface area equivalent to that of smoke outlets.
- In mechanical smoke extraction, when the air inlets are natural, their section must be such that, for the largest extracted airflow (corresponding either to the atrium or to the largest of the levels), the average air velocity is less than or equal to 2 m/s.
- When the air supplies are mechanical, their flow rate is equal to the largest extracted flow rate and the supply air speed is limited to 5 m/s.
Atrium with reduced heat potential
- The natural smoke extraction is done by openings placed in the upper part with a free surface equal to 1/100 of the base surface of the volume to be smoked, and by ensuring a minimum of 2 m².
- The mechanical smoke extraction is done with a flow equal to 1 m3/s for 100 m² of base section, and ensuring a minimum of 3 m3/s.
Other atriums :
- The floors located in the upper half of the volume are isolated by fixed construction elements.
- In natural smoke ventilation, the free surface of the smoke evacuations must be equal to 1/15 of the basic section of the volume to be cleared.
- In mechanical smoke control, the minimum hourly extraction rate is 12 times the basic volume of the atrium.
Smoke control of adjacent volumes
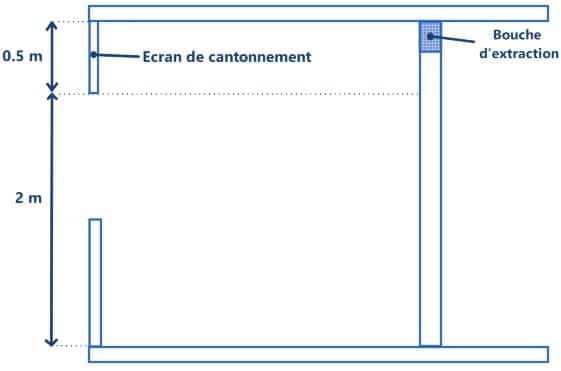
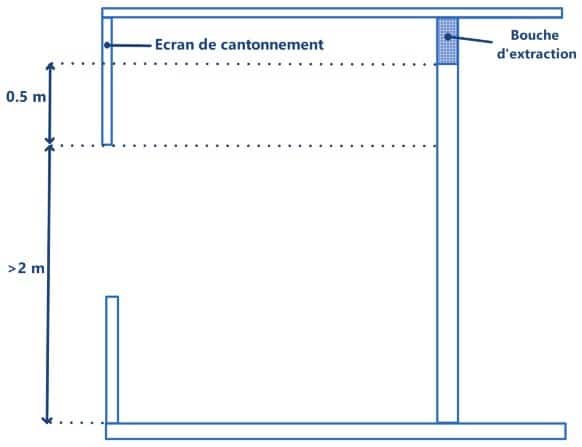
It is necessary that the interior spaces as well as the exterior corridors be equipped with a smoke extraction system, as indicated in the paragraphs below. These areas must be separated from the atrium by fixed M0 and SF 1/4 h containment screens.
The distance between the ceiling and the screen must be at least 0.50 m and for areas with a free smoke height of more than 2 meters, the screen must go down 0.50 m below the lowest point of the extract unit.
Chilled water system
Definition
Smaller atriums are located in buildings where the highest floor does not exceed a height of 8 meters from the lower level of the atrium (R+2 or R+1 with basement). They have a base with a surface of at least 5 x 5 meters.
Smoke extraction in small atriums
Smoke extraction in small atriums can be achieved in two ways:
- In a natural way, through openings placed in the height of the atrium and representing a free surface corresponding to 1/100 of the base section, with a minimum of 2 square meters.
- Mechanically, with an extracted flow of at least 1 cubic meter per second for every 100 square meters of the base section, with a minimum of 3 cubic meters per second.
- Air intakes located at ground level can be natural or mechanical. In the case of natural smoke ventilation, the air inlets must have a free surface equivalent to that of the smoke exhaust. In the case of mechanical smoke extraction, the air velocity must be less than or equal to 2 metres per second for natural air inlets and 5 metres per second for mechanical air inlets.
- If the special provisions require the removal of smoke from corridors and rooms on the periphery of the shaft, these spaces must be separated from the atrium by enclosure screens and be removed in accordance with the rules described in IT No. 246. However, the extraction must be mechanical if the building contains sleeping rooms.
Thermo aeraulics of the fire in the atrium
The following video shows a fire start for an atrium, including a free outlet area equal to 1/15 of the surface and fixed walls that isolate the upper half of the volume.
The fire used for these instructions is from the GOOD PRACTICE GUIDE FOR SMOKE ENGINEERING STUDIES. This is a fire with amaximum power of 1 MW, a linear growth of 5 minutes, a soot production rate of 5%, and a combustion enthalpy of 25 MJ/kg.
https://eolios.fr/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/atrium.mp4
Smoke extraction engineering for an atrium

