What is a data center’s digital twin?
Home » Data Center » What is a data center’s digital twin?
EOLIOS, unique know-how in Europe
- Digital twins
- Exclusive estates
- Energy optimization
- Data center supervision
- Data center
- Internal and external studies
- A passionate team
- Data center audits and diagnostics
- CFD engineering for data centers
- Thermal study of technical premises
- Generators
- Designing your data center’s digital twin
- Urban heat island impact study for data centers
- External CFD simulation for data center
- Energy optimization and PUE calculation for data centers
- Data Center Fire Simulation
- Data center audits and diagnostics
- CFD engineering for data centers
- Thermal study of technical premises
- Generators
- Designing your data center’s digital twin
- Urban heat island impact study for data centers
- External CFD simulation for data center
- Energy optimization and PUE calculation for data centers
- Data Center Fire Simulation
Our projects :
Digital twins: an asset for data center management
Optimizing costs and performance: the contribution of digital twins in data centers
Data centers have become an essential part of modern IT infrastructure, enabling companies to store, manage and process large quantities of data efficiently. However, data center management issues can be numerous and complex.
- Management complexity: Data centers are made up of thousands of interconnected devices, from servers and storage units to cooling and power supply equipment. Managing all these elements can be highly complex, requiring considerable technical expertise.
- High costs: Data centers can represent a major expense for companies, with high costs forequipment acquisition, infrastructure set -up and facilities management. Energy costs to power equipment and maintain appropriate temperatures are also significant.
- Maintenance: Maintaining the equipment in a data center is essential to guarantee the smooth operation of systems and continuity of services. This may involve planned downtime for updates and repairs, which may result in temporary service interruptions.
- Scalability: Business needs for data storage and processing can evolve rapidly, and data centers must be able to adapt to these changes. This may require additional investment in infrastructure and equipment.
- Security : Data centers can contain sensitive and confidential information, making them a potential target for cyber attacks. Installation security is therefore essential to guarantee the confidentiality and security of stored data .
That’s where digital twins come in. These virtual replicas of physical equipment and systems give data center managers a complete and accurate view of their infrastructure. Digital twins can help to continuously monitor equipment and systems, predict potential failures, improve energy efficiency and plan upgrades and repairs.
In this paper, we’ll explore how digital twins can be used in data centers to improve equipment management, reduce operating costs and enhance sustainability. We’ll also look at the benefits of this technology for businesses and organizations, as well as the potential challenges associated with its implementation.
What is a data center?
Inside a data center: powerful machines and sophisticated cooling
A data center is a facility containing a large amount of IT equipment essential to the storage, processing, management and distribution of billions of items of data.
This data is stored in storage systems such as hard disk arrays, network or cloud storage devices. They are processed in thousands of servers, which also host applications. With all this, the power of a data center can reach 100 megawatts (MW).
Data centers are particularly secure thanks to their security and surveillance systems, as they contain a great deal of confidential information. They are also air-conditioned to keep servers and other calorie-generating machines running smoothly. Numerouscooling systems are available to keep the temperature at an optimum level. What’s more, they are equipped with numerous redundant power supply systems to ensure uninterrupted operation and continuous availability of services in the event of hardware failure or power cuts. These systems can be standby generators and/or inverter systems.
These data centers play a fundamental role in the infrastructure of the Internet and modern computing, contributing to the management and availability of online services used on a daily basis.
What is a data center's digital twin?
The digital twin: a powerful virtual representation of our physical world
A digital twin is a complete and faithful visual representation of a physical object throughout its entire life cycle. It uses real-time data from the object’s sensors to continuously simulate its behavior and monitor its operations and performance, anticipate failures and make decisions.
The digital twin is based on very high-speed information transmission, such as fiber optics or 5G (or 6G network in several years’ time). It has been developed around the Internet ofThings (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI), particularly machine learning or deep learning. In effect, the digital twin makes predictions, then observes the difference between those predictions and reality, in order to learn and refine those predictions later.
The digital twin looks like a complex simulation, yet there’s a big difference between them. Simulations also model real systems and simulate their behavior. The latter can only be an indication of the actual behavior of the object or system, not the reality. The digital twin can model the exact relationship of the product or system to reality, as well as its entire life cycle, thanks to data acquired in real time.
Different types of digital twin
Digital twin technology remains broadly the same, but can be differentiated by the type of application.
Digital product twins
Digital twins make it possible to reproduce all the components of a physicalproduct in a virtual environment. This makes it possible to analyze results under different conditions and make adjustments in the virtual world, so that the next physical product performs exactly as expected in the field. This type of digital twin facilitates informed decision-making on product design and production. The ultimate aim is therefore to improve the product, avoid the multiplication of physical prototypes and minimize the potential risks associated with its design.
Digital process twins
A digital process twin can be used to verify the efficiency of a manufacturing process or production line on the shop floor before it goes into production, thanks to simulations. It offers a complete view of every product leaving the production line. Digital twins can be created for all manufacturing systems. The data collected, from suppliers and raw materials to the final product, enables us to predict when preventive maintenance will be required. As a result, manufacturing operations become faster, more efficient and more reliable.
Digital twin systems
These digital twins digitally process entire systems in order to understand processes or production lines. This also helps to determine whether synchronization between all systems is functional and effective, and to improve the efficiency of the entire production system and product.
The digital twin makes its building debut
Digital twin technology is similar to the combination of BMS (Building Management System) and BIM (Building Information Modeling) in the building industry.
BIM (Building Information Modeling)
BIM creates a digital building model that aims to centralize all data and information related to a construction project in an intelligent, interactive 3D model. This model contains not only a complex 3D model of the building, but also non-geometric features such as materials, costs, deadlines, energy performance and operation and maintenance data. Stakeholders can interact in real time on the same model, sharing a wide range of information. It’s a way of simulating and visualizing a project before it even starts, in order to identify inefficiencies and shortcomings in terms of cost and resources. BIM has a supervisory role, enabling errors to be rectified before the project is carried out. What’s more, it can be updated throughout its lifecycle, to ensure optimum building management.
BMS (Building Management System)
Efficient management of technical functions, equipment and resources is provided by BMS technology. This reduces the energy consumption of the building, known as a “smart building”, when it is in operation. The systems involved include heating, ventilation, air conditioning, lighting and security systems. The way these buildings are managed has a direct impact on their energy performance and the comfort of their occupants.
Complementarity of digital twins
These two technologies therefore complement each other, and when combined, offer even greater optimization of a building’s performance. BIM focuses on the creation and management of a collaborative digital model throughout the construction project, integrating design and construction information. BMS, on the other hand, focuses on managing the building’s technical systems during operation, to maximize their efficiency. By using these two approaches together, we can improve the planning, design, construction, operation and maintenance of buildings in a more efficient and integrated way.
Digital data center twins
The data center’s digital twin is similar to the fusion of BIM and BMS, as it is equipped with all the functions of both technologies, making it particularly comprehensive and information-rich.
Data center supervision
Comparison: data center supervision with and without digital twin
Data center supervision is conceivable without a digital twin. This is done using conventional management and monitoring systems. Temperature, humidity, power consumption and performance data from the various sensors are collected and analyzed to monitor the condition of the data center.
This supervision will be less efficient and less effective than supervision with a digital twin. In fact, the digital twin is a virtual representation in real time of all the data center’s physical and operational data, enabling complete, detailed monitoring of its performance. Its use offers many advantages:
Precision
In the absence of a digital twin, it becomes more difficult to gain a comprehensive and accurate view of all operational data and the complex interactions between data center equipment. As a result, this could lead to partial monitoring and prevent the detection of certain potential problems.
Reactivity
Problem detection can be slower when monitoring is not in real time, leading to delays in intervention and problem resolution.
Performance optimization
The ability to predict scenarios using past and present sensor data is unique to the digital twin. Without this capability, performance optimization is more limited and less precise.
The role of the digital twin in a data center
The digital twin is a revolutionary technology for data centers, optimizing efficiency, resource management, security and decision-making.
Preventing maintenance
The digital twin collects and analyzes equipment data to monitor environmental conditions such as humidity, temperature and energy consumption. It is then possible to know the state of the equipment at all times, and thus detect early signs of equipment failure. Maintenance is then possible before a major problem occurs. In the same way, the digital twin determines in advance thefuture consumption requirements of the various systems making up the data center, such as heating, ventilation, air conditioning, lighting and security systems. This perspective offers a means of managing data center capacity, so that you can expand or consolidate your infrastructure if necessary.
Energy optimization
The data center’s energy consumption is obtained from the consumption of all the equipment and systems it contains. The digital twin is able to analyze this consumption and therefore identify less efficient areas. This helps implement energy optimization strategies to reduce costs and environmental footprint.
A forecasting and planning tool
Thanks to the digital twin’s predictive power, it can be used for testing purposes. Its aim is to predict change situations even before new hardware or software configurations are made. Examples of changes are the installation of new machines, reorganization of wiring, adjustment of air-conditioning, and so on. Its predictions on the risks of errors and malfunctionsthat may occur enable us to validate or reject certain changes before their physical implementation.
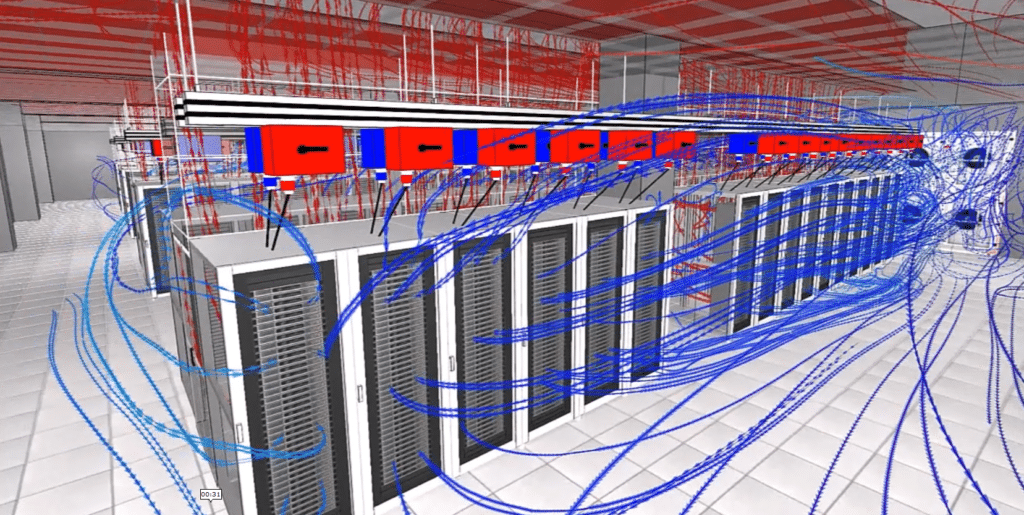
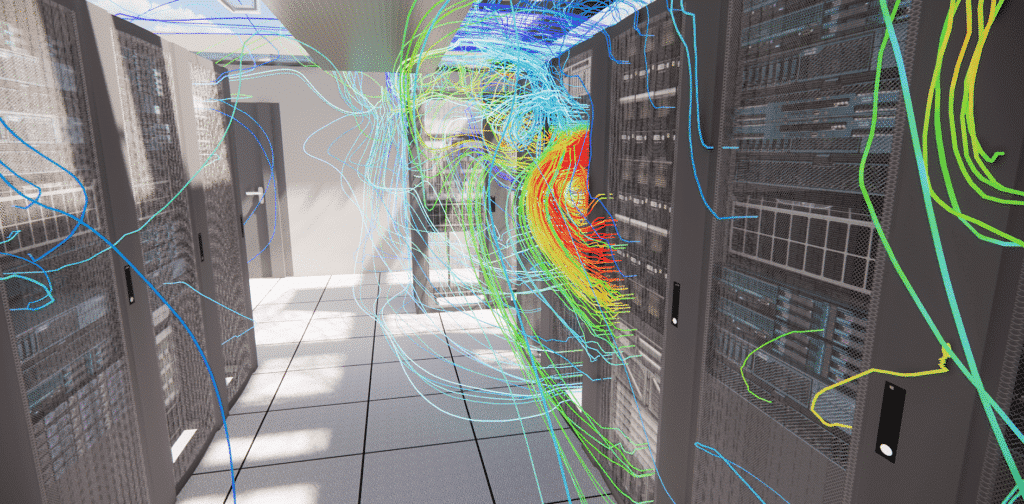
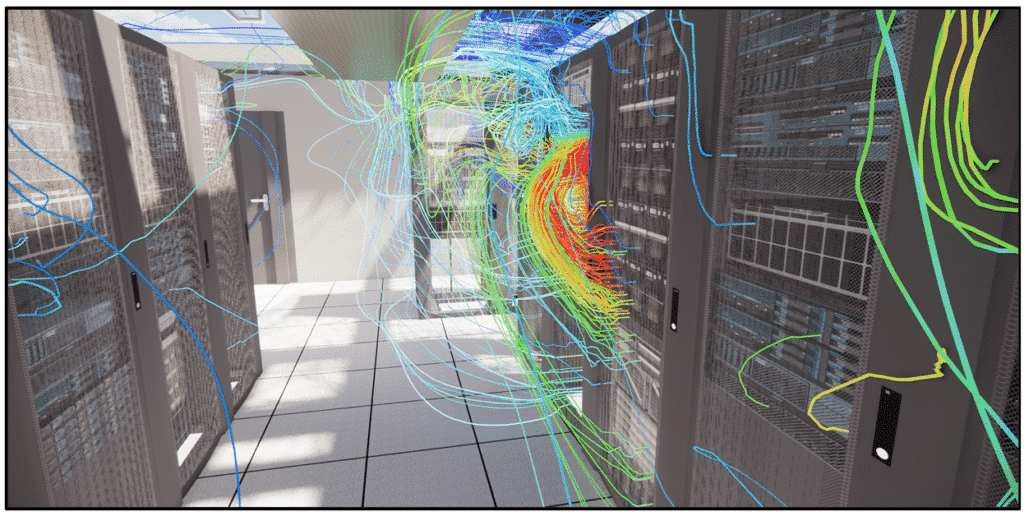
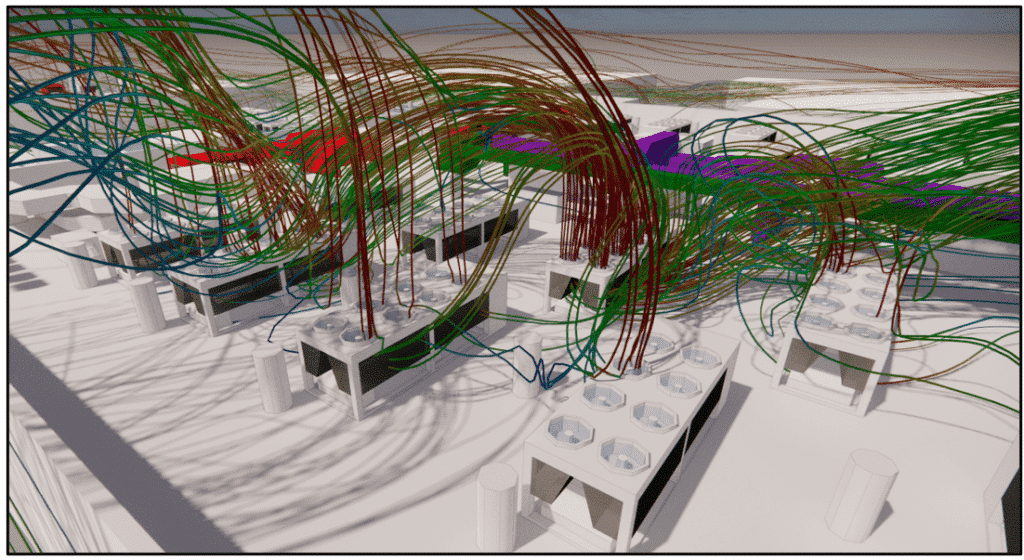
CFD study of data centers
Data center fault simulation: how does the digital twin prepare for the unexpected?
The digital twin is able to carry out thermoaerodynamic studies for data centers. Like CFD simulation, it can search for hot spots in the space and propose optimized climatic dimensioning. It is also capable of proposing energy optimizations. In fact, the digital twin can determine the ideal device blowing temperature using its simulations of different load and cooling scenarios. Reducing this temperature will reduce the energy required by the appliances, and the associated costs.
One of the key roles of the digital twin is its critical analysis. These critical analyses involve simulating several failure scenarios, i.e. the shutdown of one or more systems, and observing what happens. In the event of system failure, the temperature rises very quickly, so it’s important to have adequate systems in place to reduce this temperature.
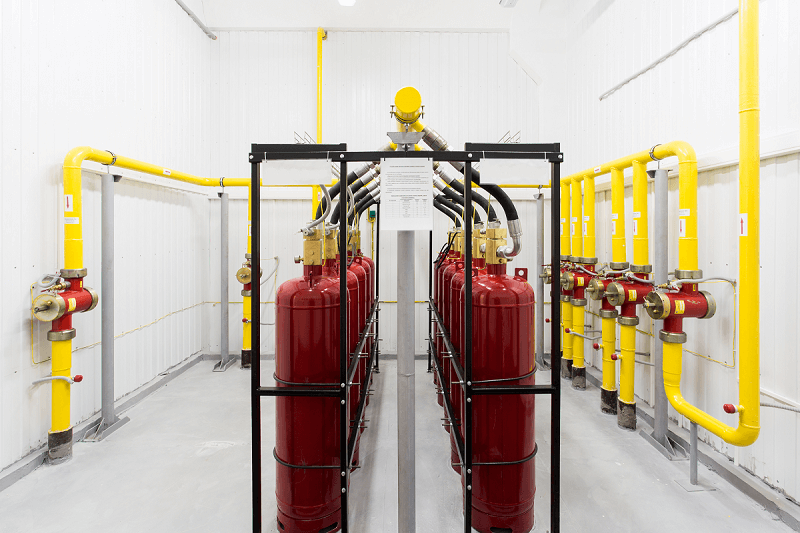
Study of fire starts and fire safety :
The digital twins also enable analysis of fire detection time, smoke propagation rate, temperature, visibility and other essential parameters.
Using detailed models based on the laws of physics and specific data on materials, equipment and fire safety systems, engineers can obtain accurate predictions of fire behavior and assess the effectiveness of the safety measures in place.
Monitoring air velocities during a fire outbreak
Monitoring temperatures during a fire outbreak
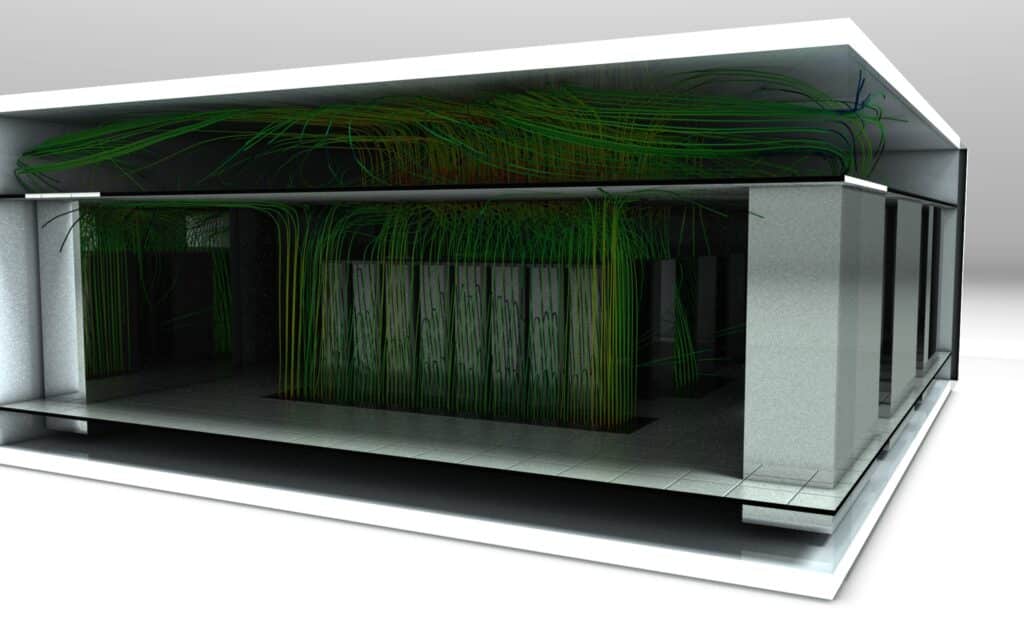
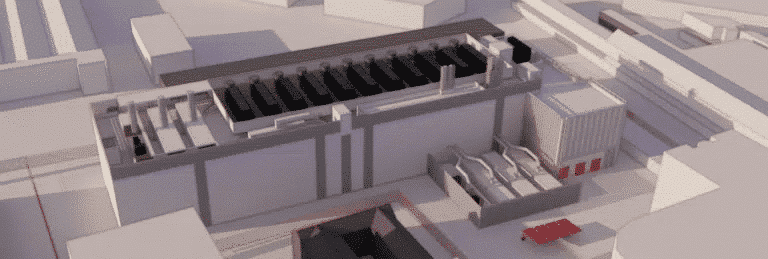
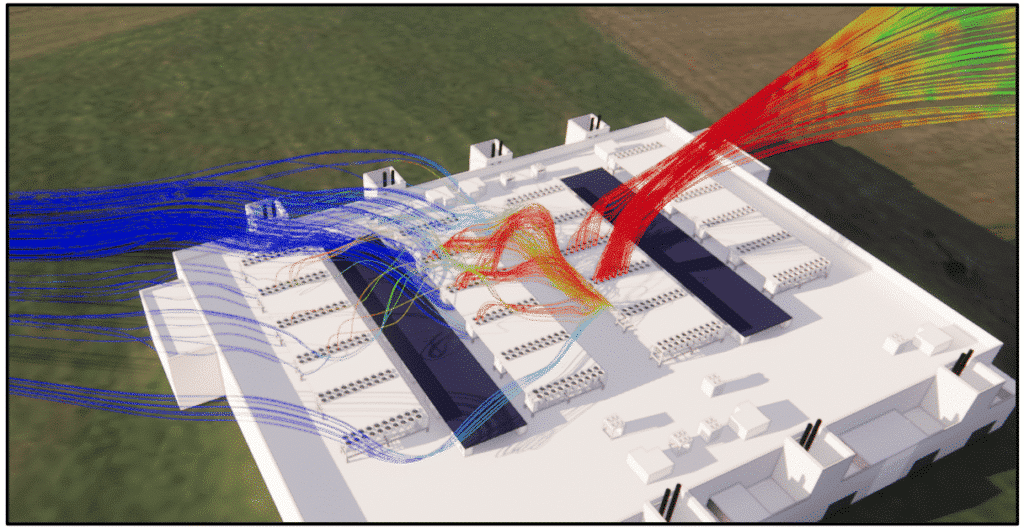
External CFD study of data centers
The importance of external CFD studies in data center resilience to extreme conditions
External thermoaerodynamic studies of data centers, carried out using CFD, involve studying air movement and winds outside the data center.
Outdoor conditions have an impact on the performance of the various equipment making up the data center.
EOLIOS carries out these external studies to ensure that the data center operates optimally even in the most extreme circumstances.
To achieve this, several scenarios were carried out in different operational modes and weather conditions. These external CFD studies make it possible to complete risk assessment, optimize design and reduce the data center’s energy consumption.
Potential challenges of digital twins not to be overlooked
While digital twins offer many advantages for data center management, their use can also present potential challenges.
- High initial cost: Creating a digital twin can be an expensive process, requiring investment in sophisticated simulation equipment and software, particularly for fluid mechanics and CFD.
- Complexity : Data centers are complex environments, with numerous interconnected systems and equipment. Creating an accurate digital twin can be a complex process, requiring an in-depth understanding of the infrastructure and its interactions.
- Need for accurate data: To be effective, a digital twin needs to be supplied with accurate, up-to-date data. This may require constant infrastructure monitoring and automated data collection, which can be difficult to implement.
- Integration with existing systems: Integrating a digital twin into existing management systems can be a challenge, as it may require significant changes to existing processes and tools.
- Confidentiality and security : Data collected by a digital twin can be sensitive, and must be protected against unauthorized access.
Introducing 6SigmaRoom software
EOLIOS uses CFD simulation to calculate and visualize air flows in 3D. We offer decision support by providing performance indices to optimize room cooling efficiency. By avoiding hot spots and providing the right amount of air to cool the electronics, the software ensures smooth operation. 6SigmaRoom’s complete data center model offers management of many other aspects of the site, such as network cablingand the electrical distribution chain.
6SigmaRoom is the most widely used CFD tool for data centers of all sizes. It’s a complete software package for the digital twin. This CFD solver is capable of creating a digital 3D representation of the physical data center. It designs and operates data centers. It can be used to simulate the impact of one or more changes on the physical capacity and cooling efficiency of a data center, and thus to simulate outages. Its aim is to design reliable, resilient infrastructures capable of operating atmaximum capacity, while improving energy efficiency.
The digital twins of data centers in a nutshell
Finally, digital twins offer enormous potential for improving data center performance and management. Using data collected from sensors and on the actual system, digital twins can help prevent breakdowns and improve energy efficiency. Data centers that adopt this technology can benefit from more accurate monitoring, lower operating costs and greater long-term sustainability.