Blind controls
Accueil » Air & Wind » Blind controls
EOLIOS designs or rectifies the sizing and regulation of your blinds:
- Study of anemometer positioning
- Site audit with portable anemometer
- Designing blind control laws
- Numerical modeling of extreme winds
- Design of natural ventilation control systems
- List item
Continue navigation :
Our latest news :
Our projects :
Our areas of expertise :
Blind control sizing
EOLIOS brings its experience in urban aeraulics and large structures to bear on the efficient regulation of awnings. This regulation is crucial to the preservation of outdoor awnings.
Awnings provide effective protection from the sun.
Awnings are motorized and regulated by anemometers, which automatically raise the awning if the wind exceeds a certain threshold.
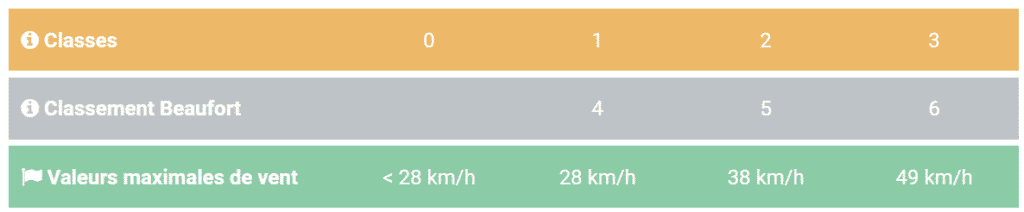
European standard 89/106/EEC, “Construction Products”, specifies the performance requirements to be met by external awnings installed in buildings.
The standard requires an indication of the wind speed the awning can withstand.
A classification into four classes has been established to make it easy for consumers to tell the difference.
Each class has its own maximum wind speed given in Beaufort or km/h (see table below).
Cold aisle / hot aisle design
The Beaufort scale is an empirical measurement of 13 degrees (0 to 12) of average wind speed over a ten-minute period, used in maritime environments.
An anemometer continuously analyzes wind intensity.
As soon as the tolerance threshold is exceeded, the awning automatically retracts. To obtain accurate data, it’s essential to choose an environment free of obstacles and aeraulic disturbances.
Analysis of correlated wind speeds
As you might expect, the wind measured by the anemometers is not consistent with the wind arriving at the blinds, and can lead to premature destruction of the blinds.
Indeed, the wind speeds are specific to each point of the roof and the facades of the building.
Thus, the air speeds at the level of the anemometers are not necessarily correlated with the speeds on the facade where the blinds are located.
Local phenomena modify the distribution of the flows which can disturb the functioning of the measuring systems.
Our studies take into account all the geometric details required to solve the problem.
Several levels of scale – building (neighborhood), terrace (area), windbreak (specific elements) – are refined separately to increase resolution in the study areas.
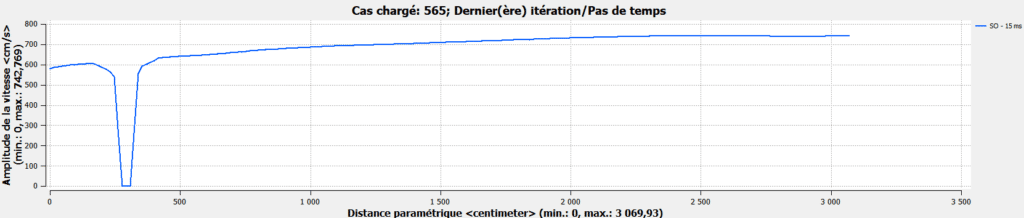
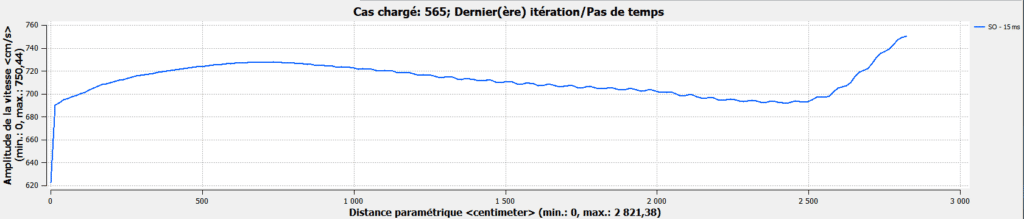
Analysis tables will show wind speed profiles at blinds or in critical areas, and will be compared with the anemometer measurement point.
Example:
Depending on the results of the analyses and the final placement of the anemometers, a reprogramming law will be proposed, taking into account the most unfavorable winds for the blinds.
On-site wind measurement :
We can carry out smoke tests to understand and locate the specific wind trajectories at blind and anemometer level (terrace and roof area).
We then usually produce a series of diagrams to explain the broad outlines of the wind on site, the specific aeraulics per floor and the behavior of the anemometers in relation to the blinds.
These smoke analyses are played back on video, giving the operator a general understanding of the impact of wind on the building (for a single wind) in relation to the anemometers.
The blinds subjected to the most critical tearing are identified.
At the same time, we carry out portable anemometer measurements at blinds and anemometers, so that the operator can study the feedback from the BMS.
This also enables a more precise understanding of aeraulic effects in physically accessible areas.
The positioning of each anemometer is audited, and site effects are explained on the basis of observations.
Simultaneous anemometer readings are taken to record scale factors between accessible blinds and anemometer zones.
EOLIOS generally visits the site twice for two similar audits in different wind conditions.
These audits are therefore dependent on weather conditions and can only be planned 48 hours in advance.
Site safety conditions permitting , EOLIOS engineers can operate independently.
Beyond the simple measurement report, EOLIOS will recommend, in view of its experience and its understanding of the site, the modification of the location of the anemometers. We will also alert the operator, if the new positioning of the anemometers may include wind origins for which its results may be obsolete.
We would like to point out that this measurement and analysis campaign enables us tooptimize the operation of the anemometers, but cannot provide an exhaustive analysis of the phenomena, as only the accessible zones can be studied. As an option, we can also carry out numerical studies to gain a more detailed understanding of aeraulic phenomena.
Video – Study of the effects of wind in cities – La Défense