Industrial Natural Ventilation Design
Home » Industries » Industrial Natural Ventilation Design
Natural ventilation engineering is based on precise phenomena that can be mastered!
EOLIOS brings you its CFD expertise to improve thermo-aerodynamic comfort, extract pollutants and optimize natural ventilation in industry.
- Sizing static aerators
- Ventilation shaft design
- Energy optimization
- Improved thermal comfort
- Improving air quality
- Sizing of filtration systems
- Pollutant extraction
- Evacuation of water mists
- Evacuation of hot air masses
Continue navigation :
Our latest news :
Our projects :
Our areas of expertise :
Designing natural ventilation in an industrial context
Principle of natural ventilation
In industrial facilities with large heat sources, such as glass and steel plants, natural ventilation uses the heat gains from the production process itself to create sufficient motive power.
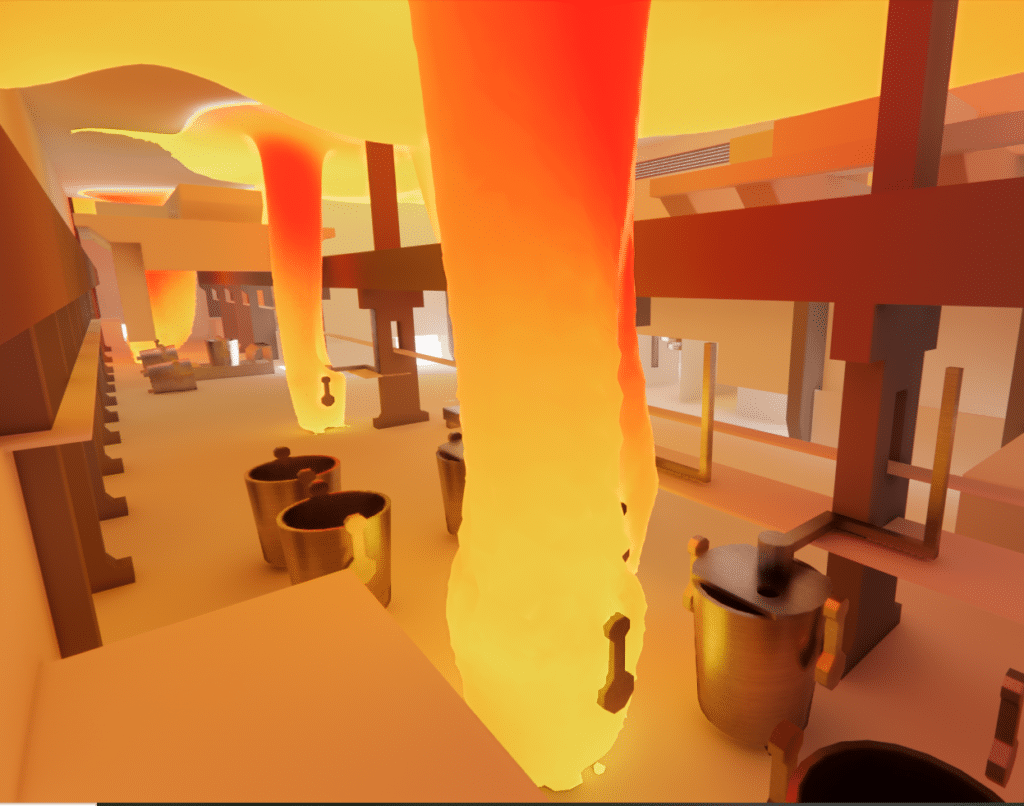
Ventilation of a plant containing furnaces operating at the extremely high temperatures required for glass production is a major technical problem. Even the best insulated furnaces give off large amounts of heat inside the facility, resulting in very high heat gains to the indoor air.
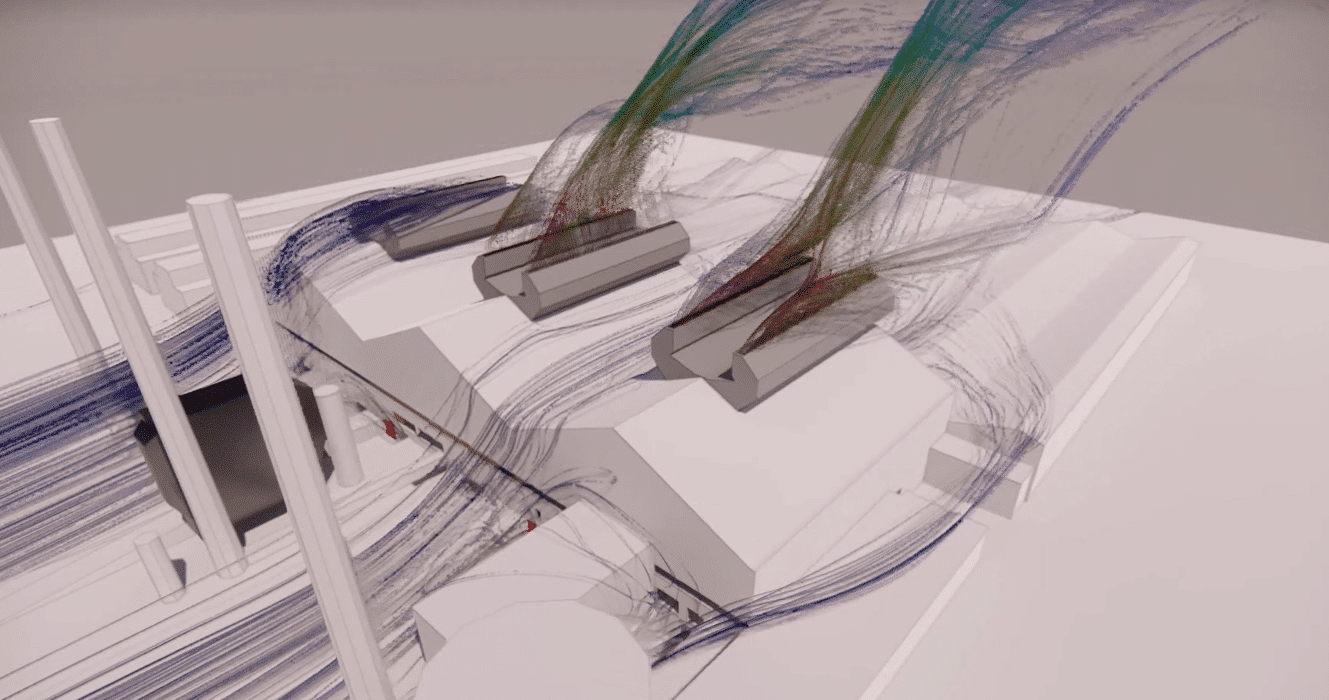
Current lines colored by temperature - Glassware
Risk of poor ventilation management in industrial environments
Every building, including glassworks, is assigned a critical temperature which, if exceeded, can damage the structure, especially the roof, where heat gains are greatest. Any excess heat that could raise the temperature to critical levels that could lead to deformation or damage fires if grease has built up over time.
On the other hand thermal comfort must be maintained at optimum levels for workstations, or acceptable levels for temporary intervention zones (above furnaces, for example). To do this, air must be released into the atmosphere to ensure the continuous operation of the system.
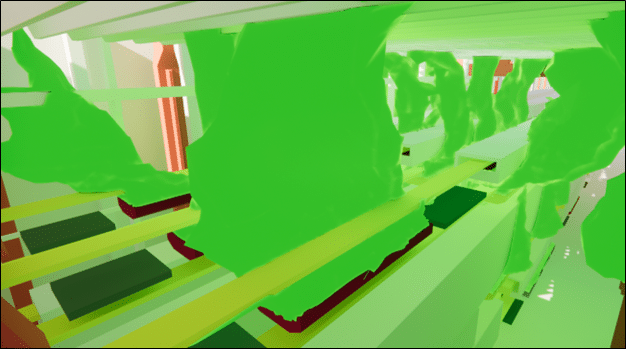
Video - Temperature isosurfaces - Steelworks
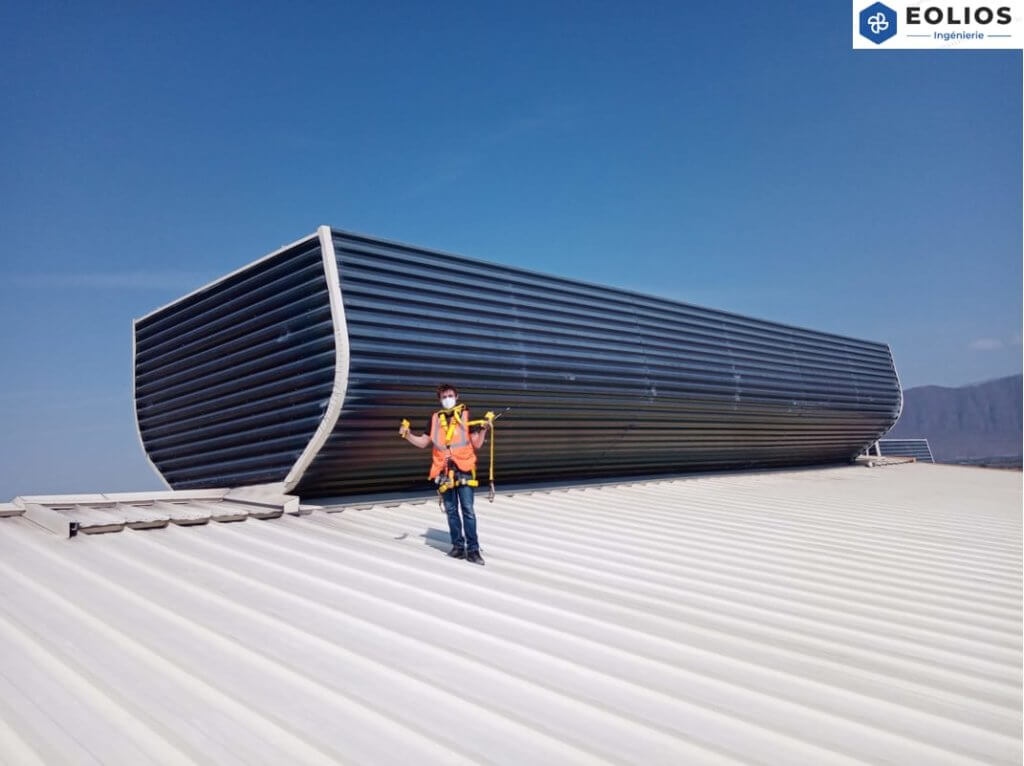
Sizing of static natural ventilation aerators
The right dimensioning of static aerators is essential foreffective natural ventilation in a building. These devices play a key role in managingincoming and outgoingair, ensuring optimal air circulation.
Incorrect sizing can lead to overheating,excessive humidity or poor indoor air quality, making the environment uncomfortable for occupants. Depending on the configuration of the building, its use and local climatic conditions, it’s crucial to choose the right aerators in terms of size and positioning.
Correct sizing not only ensures that thermal comfort and air quality requirements are met, but also maximizes energy savings, by reducing the need for air conditioning or heating.
Studies on natural ventilation systems
Airflow characterization
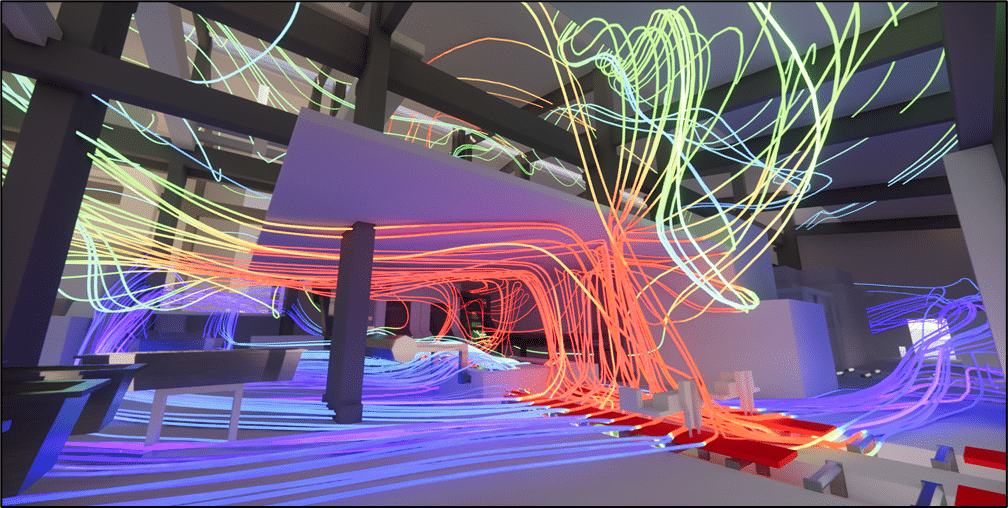
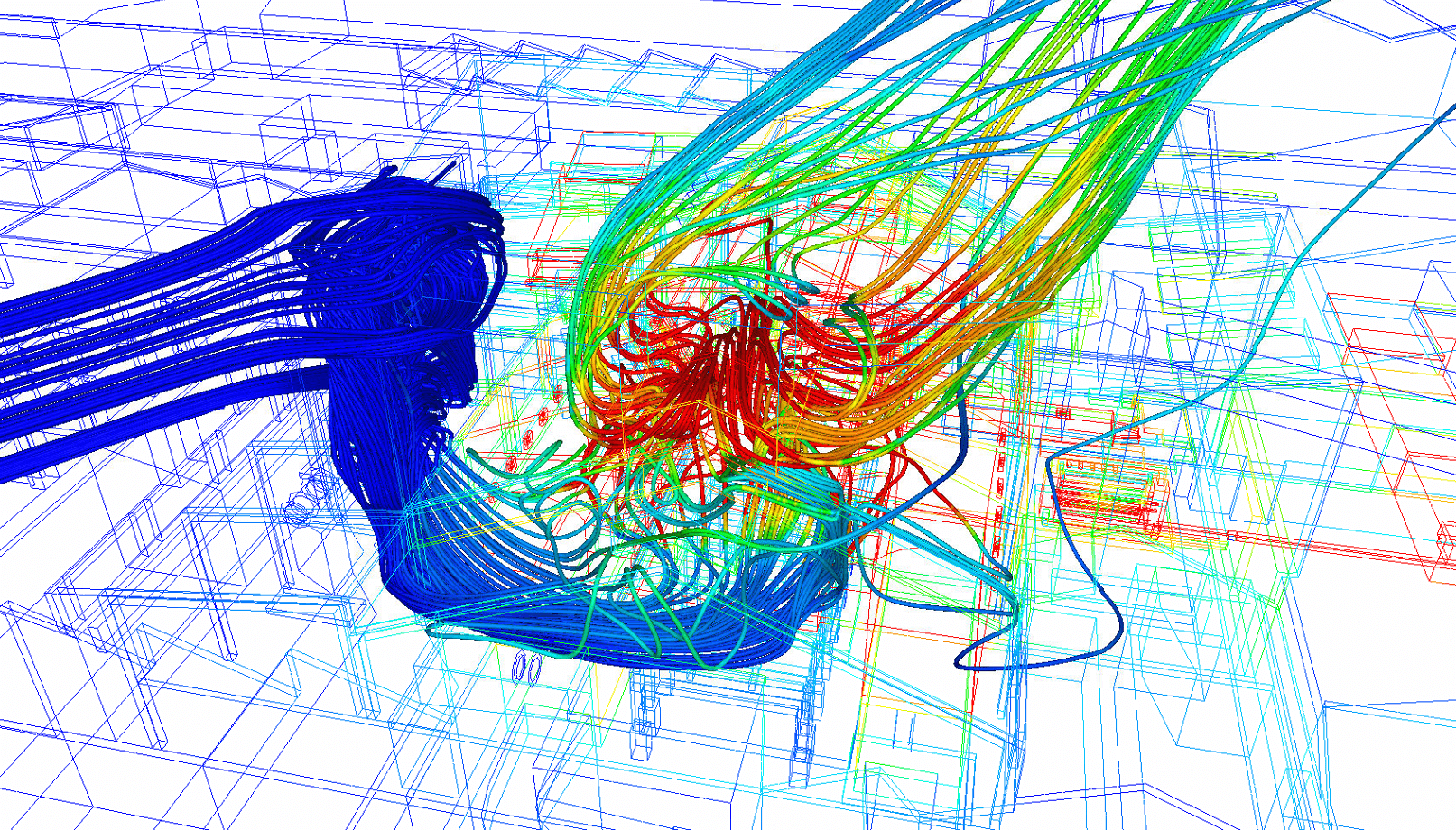
Calculation by CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics) calculation provides precise modeling offresh air flow, air velocities at doors and static ventilators (Robertson type), as well as extracted air flow through the latter. Thanks to this numerical simulation, it is possible to visualize and optimize air circulation within the building, taking into account various parameters such as space geometry, openings and climatic variations. Particular attention must be paid to air velocities at doors and static ventilators, as incorrect sizing or placement can lead to thermal discomfort or poor ventilation.
In addition, poorly designed vents can increase the risk ofuncontrolled air ingress, disrupting indoor air management and creating areas of overheating orexcessive humidity. CFD calculations help prevent these risks by optimizing the placement and sizing of openings, thus ensuring smooth, efficient operation of the natural ventilation system.
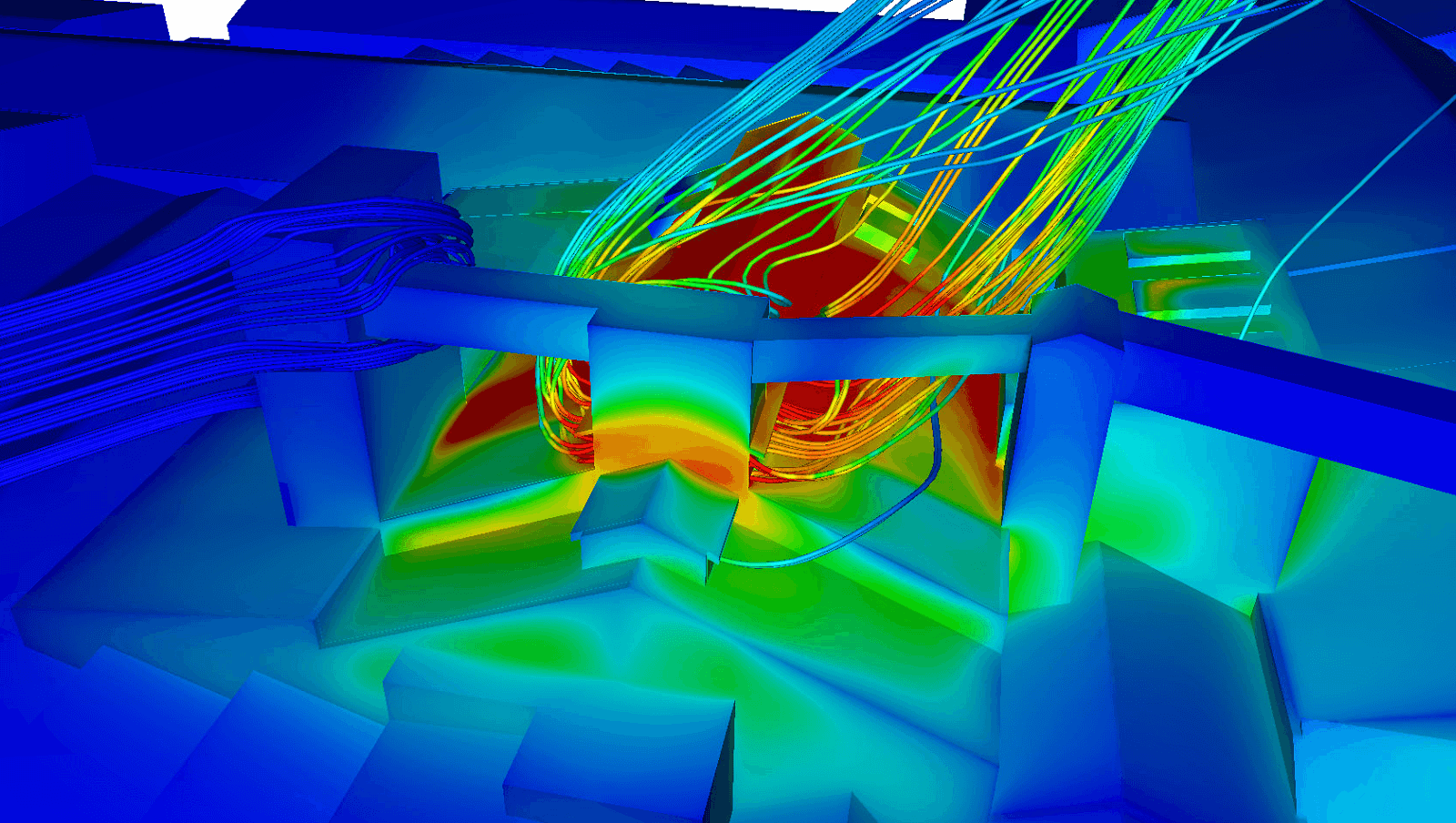
Wall temperatures and current lines colored by temperature - Aluminum plant
Thermal study of heat dissipation through natural ventilation channels
Thermal studies to quantify the impact of high-temperature processes are essential in the context of natural ventilation, particularly in industrial or commercial buildings where thermal processes generate high levels of heat.
These processes, such as furnaces, boilers or engines, can lead to a significant rise in temperature inside the spaces concerned, affecting the thermal comfort of occupants and the efficiency of natural ventilation. A thermal analysis can simulate heat distribution in the building and determine the impact of these heat sources on air circulation, optimizing the sizing of vents and openings.
These studies also enable us to identify areas of overheating and implement solutions to maximizeheat dissipation andwarm air management, while guaranteeing good air quality and optimum comfort. Thanks to this approach, natural ventilation can be adapted to the specific requirements of thermal processes, while minimizing energy consumption.
Video - Heat loss study - Steelworks
Tracing and extracting pollutants
Tracking andevacuating pollutants using CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics) are key tools for optimizing the efficiency of natural ventilation in a building.
CFD simulation can be used to model the behaviour of pollutants (such as fine particlesvolatile organic compounds or toxic gases), taking into account the various sources of contamination and environmental parameters.
This approach makes it possible to precisely visualize their trajectory through the air, identify areas of high concentration and determine the best strategies for efficiently evacuating them to the outside. By optimizing the placement of vents and openings, and adjusting the flow of incoming and outgoing air, CFD helps ensure air circulation that promotesrapid evacuation of pollutants while maintaining optimum thermal comfort. This approach helps create healthier indoor environments, with controlled air quality, while reducing the environmental impact of ventilation.
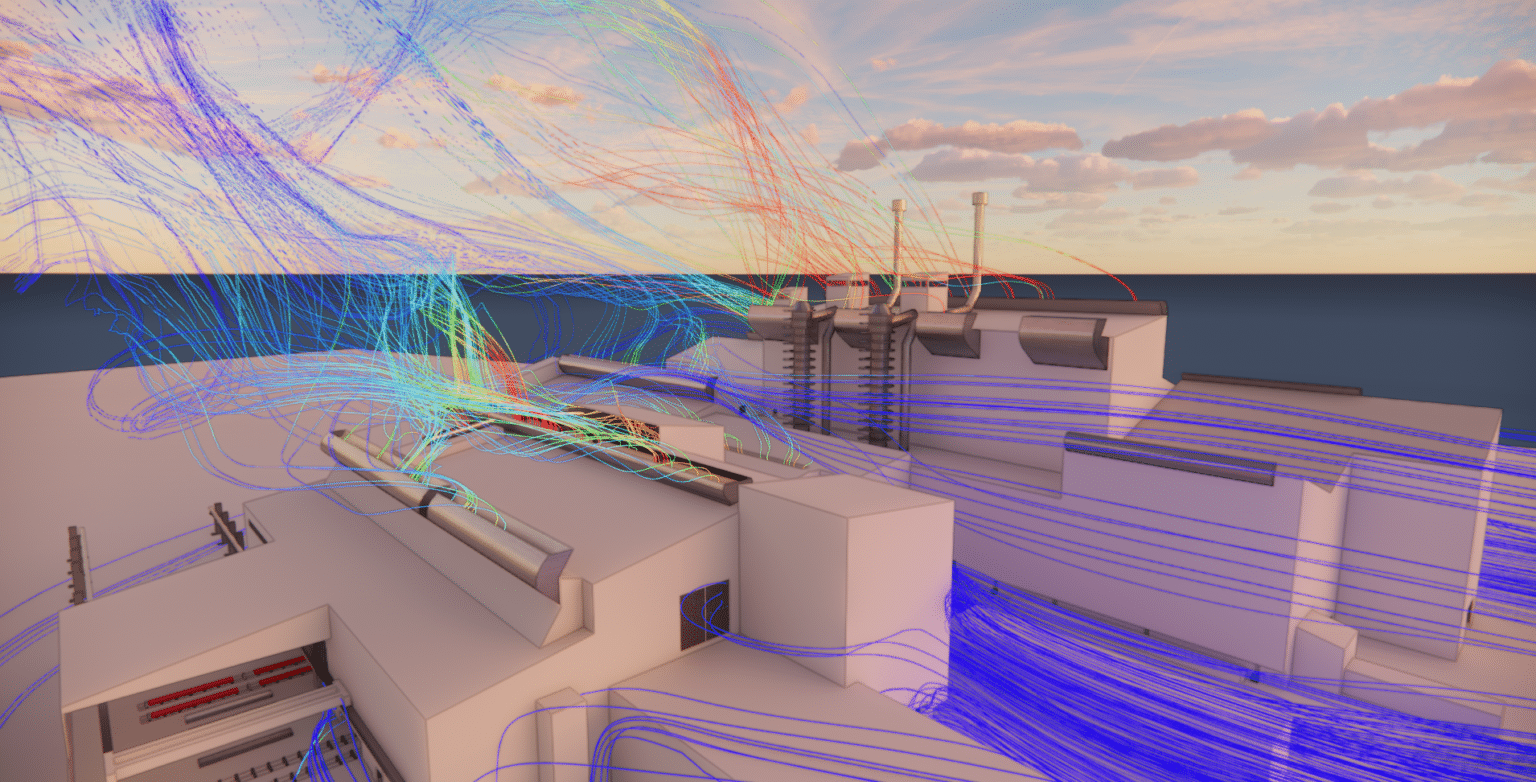
Influence of weather conditions
Weather conditions play a decisive role in the efficiency of a building’s natural ventilation. Outside temperature, wind speed andrelative humidity have a direct impact on indoor air circulation.
For example, hot days can increase the thermal draught effect, promoting the rise of warm air and better evacuation of stale air. Conversely, cooler or windier days can improve thesupply of fresh air, but can also lead to uncomfortable draughts if ventilation is not well designed.
The sizing of openings, ventilators and ventilation ducts must therefore take into account local climatic variations to adapt to different weather situations. CFD simulation can be used to predict the impact of outdoor conditions on indoor air circulation, and thus optimize the ventilation system to guarantee optimum comfort all year round, while reducing energy consumption.
Automated natural ventilation
Automated natural ventilation combines the principles of natural ventilation with advanced technologies to automatically regulate airflow according to the building’s actual needs. Thanks to integrated sensors that measure parameters such as temperature,humidity and air quality, the system adjusts the opening of ventilators and windows in real time to promote optimum ventilation, while maintaining constant thermal comfort.
In particular, this approach enables the ventilation system design to adapt to meteorological variations, but also to avoid oversizing the systems, in particular by reducing excessively high air speeds at operator level, which can generate discomfort.
Improving working conditions for operators in industrial environments
Optimizing thermal and aeraulic comfort
Improving air quality
Improving air qualityair quality is a fundamental aspect of natural ventilation, which aims to ensure a healthy indoor environment by promoting constant, controlled air renewal. By exploiting the natural principles of thermal draft and convection, natural ventilation reduces the concentration of pollutants (such as fine particles, volatile organic compounds or carbon dioxide) while maintaining a comfortable indoor temperature.
The right sizing and positioning of openings and ventilators ensure optimum air circulation, efficiently evacuating stale air and introducing fresh air without resorting to energy-intensive systems. In addition to preventing problems of poor air quality, this natural approach reduces the risk ofexcessive humidity and mold, contributing to a healthier, more pleasant environment for its occupants, while minimizing the building’s ecological footprint.
Compliance with natural ventilation standards and regulations
Energy optimization for industrial buildings
Compliance with occupational exposure limit values (OELVs)
This system not only ensures compliance with exposure limit values but also ensures a healthy healthy working environmentenvironment, reducing the risks associated with poor indoor air quality, such as respiratory disorders or occupational occupational illnesses.
VLEP studies can also be used to identify the PPE needed to ensure compliance with VLEP in the most polluted areas. The natural ventilation thus becomes an important asset in protecting the health health of occupantswhile promoting a comfortable working environment comfortable and safe working environment.