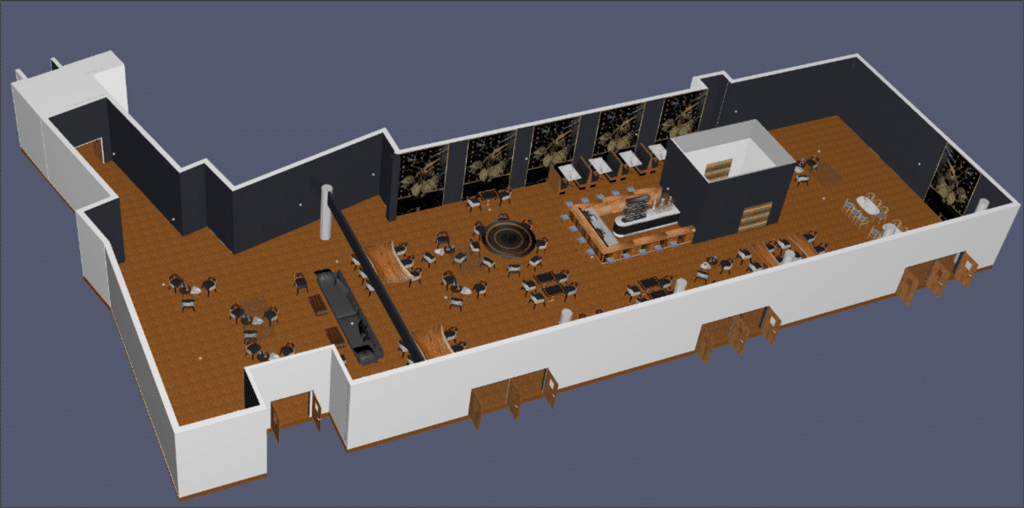
Home » Smoke control » Smoke control engineering (ISI) » Smoke control engineering – Restaurant area – Type N
Smoke control engineering – Restaurant area – Type N
ISI study (fire safety engineering) - Verification of smoke extraction efficiency in a restaurant area
As part of a building restructuring project, EOLIOS is leveraging its expertise in numerical simulation, in particular through the application of CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics) techniques, forfire safety engineering (FSE). Our approach in this study focuses specifically on the qualification of smoke extraction systems in the context of a design change. By modeling aeraulic and fluid dynamic movements, CFD simulation offers crucial information on the smoke and temperatures that will develop in and around structures.
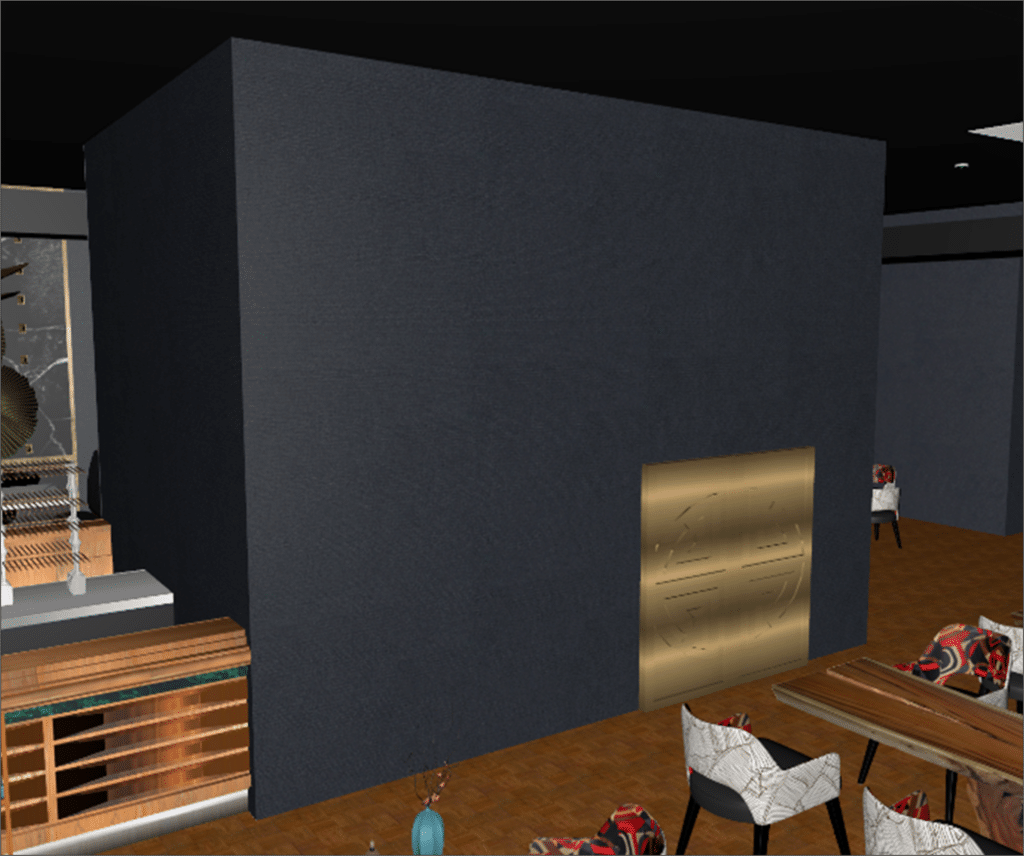
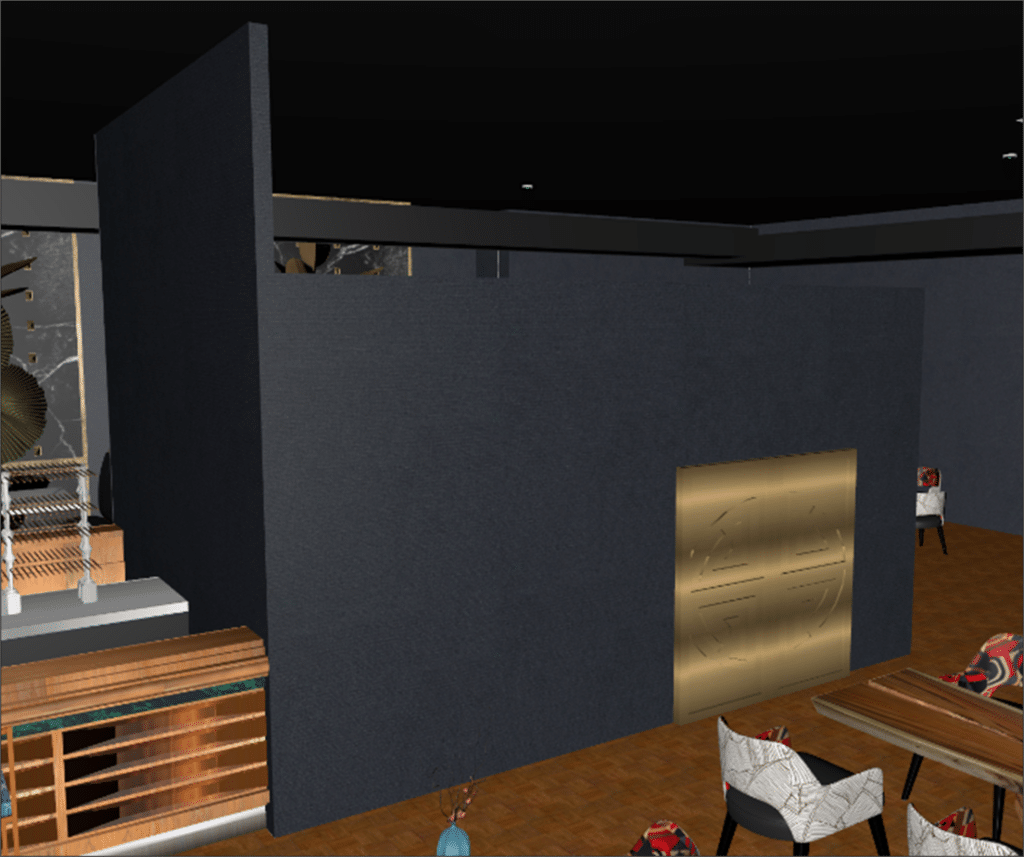
The core of this study is to evaluate the optimal operation of smoke extraction systems with the installation of full-height partitions in a building. Occupant protection and safety are key priorities and a major challenge for the project. To assess smoke extraction functionality, two configurations were studied: one with four full-height partitions and the other combining one full-height partition with three other partitions partially open in height.
EOLIOS is committed to providing customized solutions through advanced CFD simulations, carefully evaluating all identified issues to ensure maximum safety of your smoke extraction system.
Smoke control & fire safety
ISI study (fire safety engineering) - Verification of smoke extraction efficiency in a type N restaurant area
Year
2025
Customer
Unibail
Location
France
Typology
Smoke Control & Fire Safety
Continue navigation :
Our other projects :
Latest news :
Technical file :
Our expertise:
Smoke and its dangers - Commitment to safety and compliance with standards
In the event of a fire in a building, smoke represents a major hazard because of its ability to obstruct escape routes, its toxic fumes and its ability to reduce visibility. In fact, “smoke inhalation is the main cause of morbidity and mortality among fire victims” (www.alpes-maritimes.gouv.fr).
Compliance with safety standards such as NF EN 13.945 and NF EN 13.571 is essential to reduce these risks and ensure occupant safety. EOLIOS works in compliance with these regulations, while integrating its CFD simulation expertise to assess thesmoke ventilation engineering of the study.
The 5 dangers of smoke
- Toxicity : Smoke is composed of elements highly toxic, such as monoxide and carbon dioxide, which can cause serious illness. serious health problems, including suffocation irritation and critical drop in ambient oxygen levels. Even a slight decrease in oxygen can lead to severe disabilities, or even dead.
- Opacity : The carbon particles present darken the smoke, making itdifficult to evacuate and increasing the panic. This opacity can also compromise the effectiveness of rescue operations and provoke additional property damage.
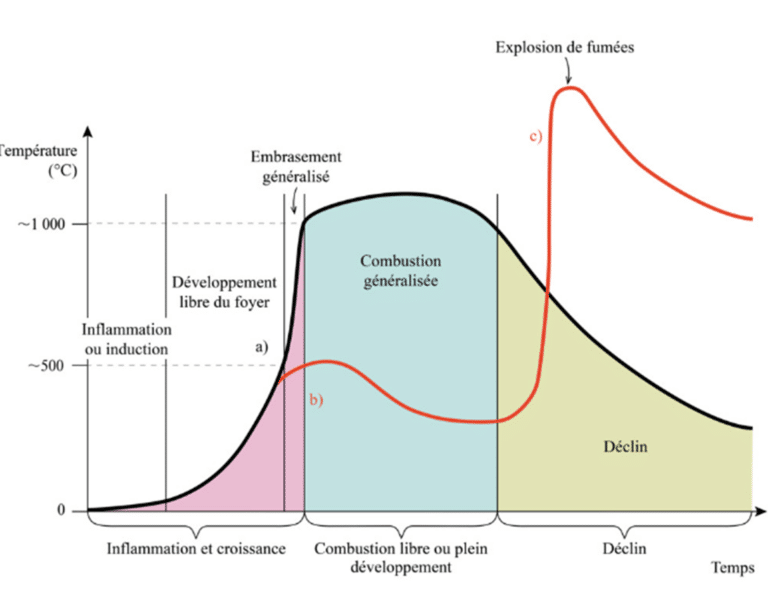
- Flammability : Smoke can transport fire by convection and radiation. Phenomena such as theGeneralized Flash Fire (GFE) and theSmoke Explosion (SE) highlight its hazardous in enclosed or semi-enclosed spaces.
- Heat: Smoke can cause severe burns and property damage due to the high temperatures it contains.
- Mobility : The propagation speed of smoke, generally between 0.20 cm and 1 m/s, can be calculated to assess the time required to invade a given space.
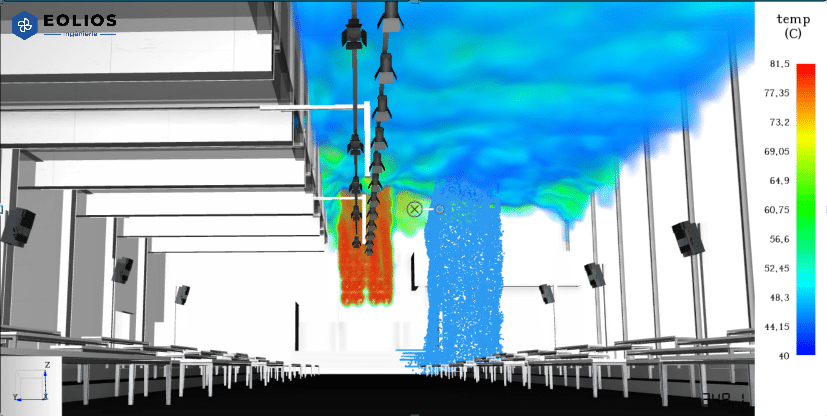
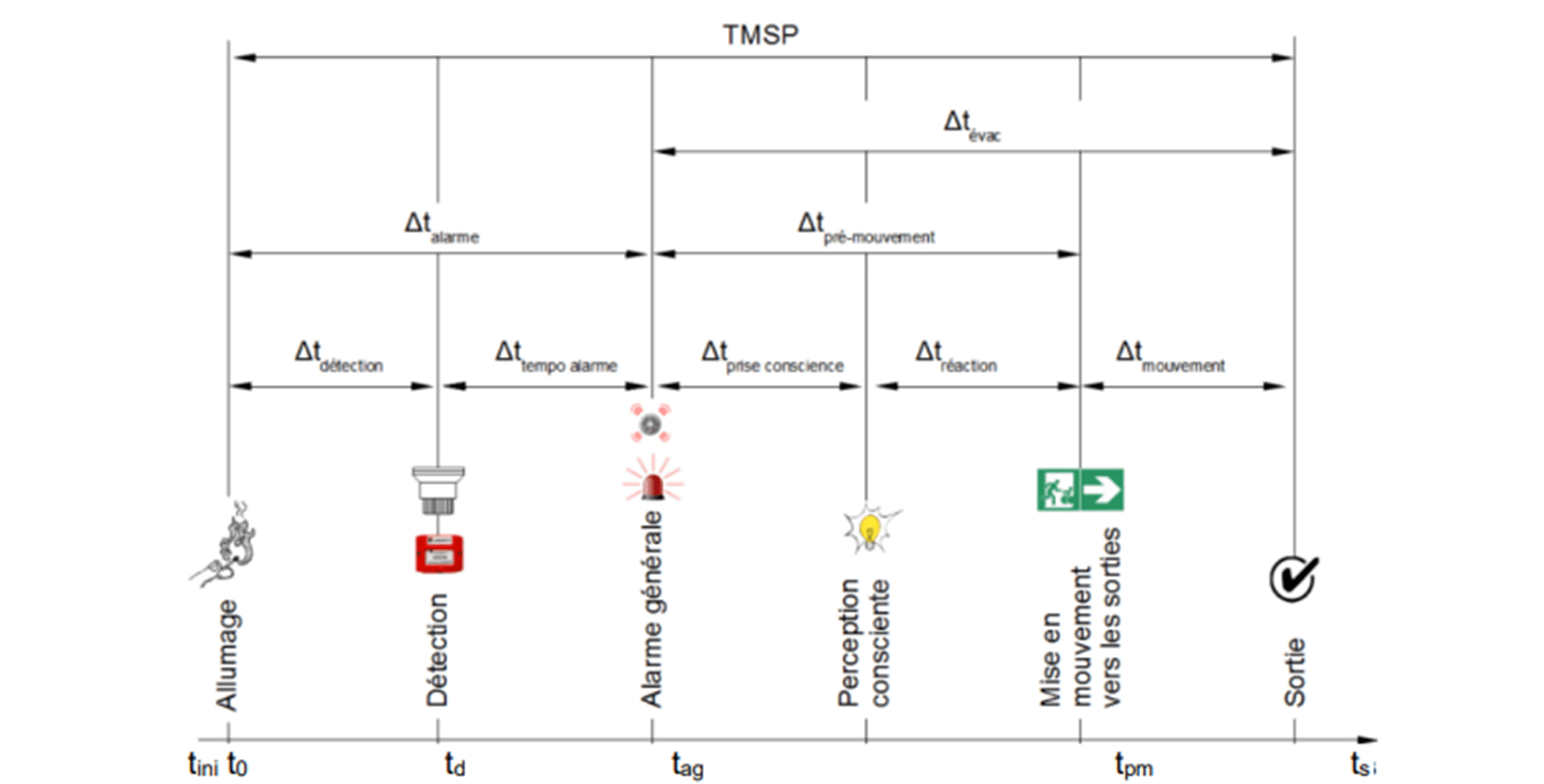
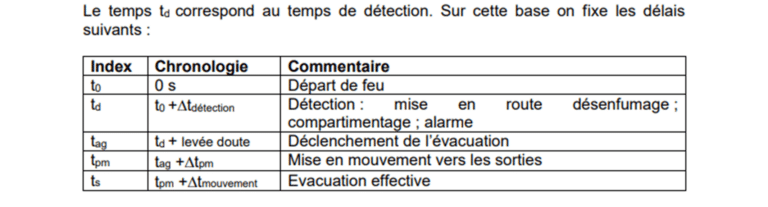
Using the CFD, it is possible to forecast smoke movements, to ensure that the emergency exits remain accessible and the smoke extraction systems effectively reach safety objectives. As part of this study, which involves the evaluation of the creation of new spaces with natural ventilation, EOLIOS provides the project owner with its expertise to observe theeffectiveness of the smoke extraction system. Our aim is to point out any potential risk.
The now moisture-laden air escapes from the tower via fans at the top. The cooled water, meanwhile, is collected in a tank at the bottom of the tower, then pumped back to the cooling system. This process takes place continuously, ensuring efficient cooling and the maintenance of a stable temperature inside the building. The main objective is to ensure efficient cooling of the offices by validating the sizing and layout of the TAR systems on the roof. The aim is also toimprove the overall performance and energy efficiency of the RACs in order to minimize energy consumption. The
EOLIOS expertise: Fire characterization using CFD simulation
Developing fire scenarios
This initial phase is crucial for defining the essential stages of each fire scenario, anchoring parameters such as :
– Focus position and characterization: Strategic placement according to simulation objectives and systems under study.
– Structural and system variables: These have a direct influence on the development and spread of fires.
The methodology employed is based on a volume heat source model, in which the essence of the combustion phenomenon(flame) is not simulated, but the thermal and toxic effects resulting from combustion are integrated. This model imposes a source of heat and toxic products in a predetermined volume, representing the flame zone of the fire.
Importance of the study scenario
Each study scenario is composed of a design solution, initial conditions, and a localized fire scenario. A single fire scenario integrates
Strategic home locations
The ability to accurately assess the sizing of smoke extraction systems depends largely on the strategic location of the fireplaces. We have adopted a
3D modeling for smoke extraction
As part of the study, particular attention is paid to precise, detailed 3D modeling of the interconnections between the building’s various spaces, such as staircases, corridors and doors. This is an important step in identifying and analyzing all elements likely to interfere with the passage of smoke. We guarantee an
In the CFD model, the emphasis is on reproducing fixed obstacles such as permanent furniture. This approach makes it possible to focus the analysis on fluid dynamics and accurately simulate smoke extraction paths.
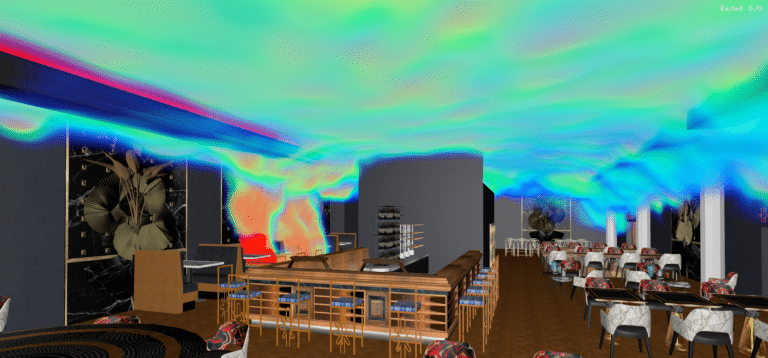
Smoke extraction simulation results: Design validation
SDS modeling of a restaurant fire
SDS modeling of a restaurant fire
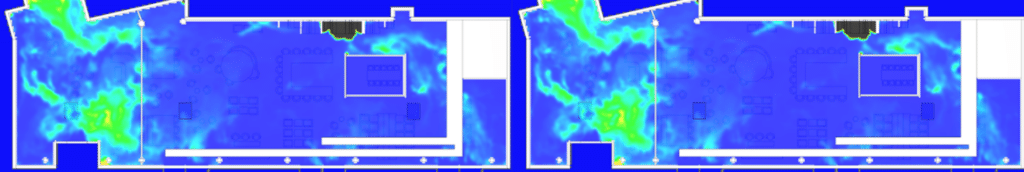
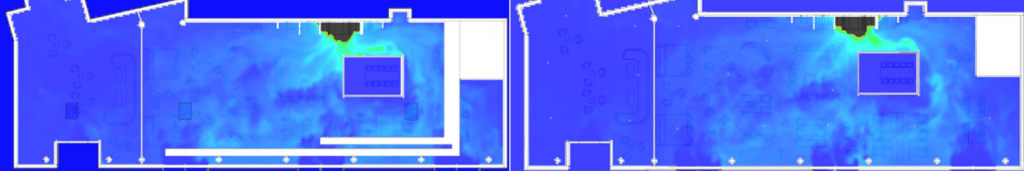
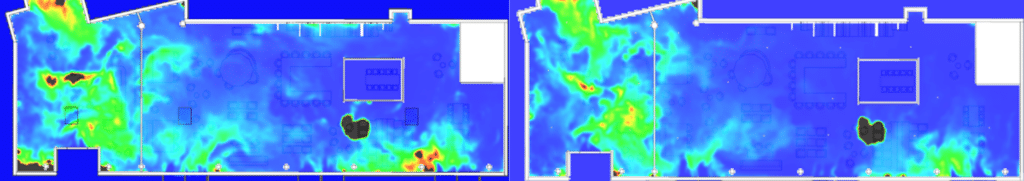
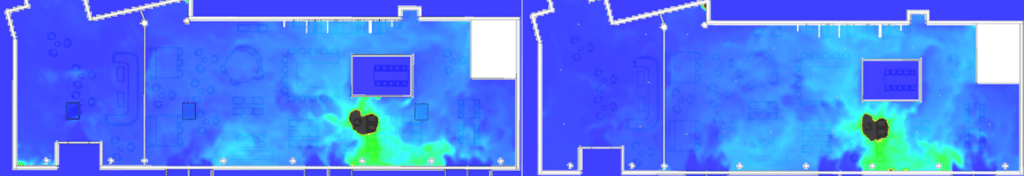
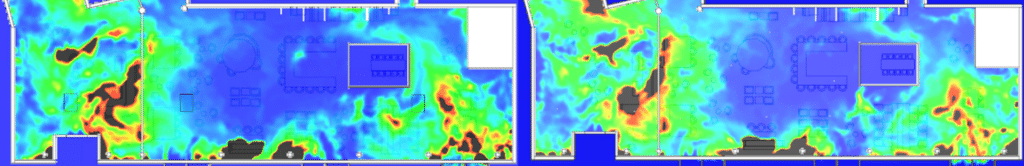
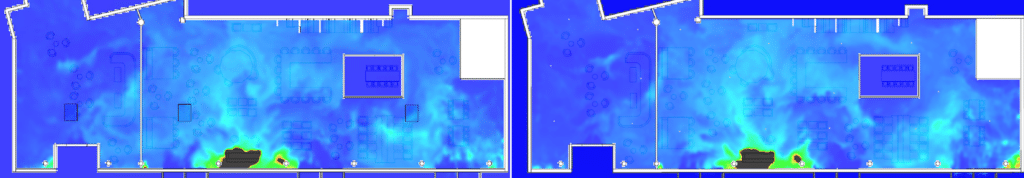
EOLIOS - Smoke control design office
At EOLIOS, we are dedicated to supporting you in the design or evaluation of your smoke extraction systems, ensuring the safety and protection of your buildings and their occupants. We are committed to precise, efficient system design.
Our expertise in CFD simulation enables us to analyze aeraulic dynamics, identifying smoke trajectories and potentially critical areas where accumulations can occur. By integrating these analyses, we ensure optimum airflow distribution and minimize points where smoke could stagnate, thereby reducing risks to human safety.
We rigorously assess the efficiency of smoke extraction systems, enabling you to validate and optimize their performance in the most unfavorable scenarios.
Continue on this topic
Video summary of the study
Summary of the study
At EOLIOS, we are dedicated to supporting you in the design or evaluation of your smoke extraction systems, ensuring the safety and protection of your buildings and their occupants. We are committed to precise, efficient system design.
Our expertise in CFD simulation enables us to analyze aeraulic dynamics, identifying smoke trajectories and potentially critical areas where accumulations can occur. By integrating these analyses, we ensure optimum airflow distribution and minimize points where smoke could stagnate, thereby reducing risks to human safety.
We rigorously assess the efficiency of smoke extraction systems, enabling you to validate and optimize their performance in the most unfavorable scenarios.
Video summary of the smoke ventilation engineering mission
Discover other projects in smoke and fire control
Engineering smoke extraction in a data center
Smoke control engineering – Restaurant area – Type N
Fire engineering – Fashion show
Losses – CNIT
Smoke control engineering – Theater
Data Center – GAZ NOVEC
Smoke extraction – CHU
ISI – Offices – Grand Army
Smoke extraction plenum – AF1
Smoke extraction plenum – AF2